Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can “just run” —— 能快速创建出生产级别的Spring应用
Spring Boot 官方
Spring Boot 官方手册
Create stand-alone Spring applications:创建独立Spring应用
Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files):内嵌web服务器
Provide opinionated ‘starter’ dependencies to simplify your build configuration:自动starter依赖,简化构建配置
Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible:自动配置Spring以及第三方功能
Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration:提供生产级别的监控、健康检查及外部化配置
Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration:无代码生成、无需编写XML
Spring Boot是整合Spring技术栈的一站式框架
Spring Boot是简化Spring技术栈的快速开发脚手架
Java 8 & 兼容Java14
Maven 3.3+
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 <parent > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4.RELEASE</version > </parent > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <fork > true</fork > <addResources > true</addResources > </configuration > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
spring-boot-maven-plugin插件以Maven的方式为Spring Boot应用提供支持,能够将Spring Boot应用打包为可执行的jar或war文件,进行相应部署后即可启动Spring Boot应用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.zhao.boot;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplication public class MainApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.zhao.boot.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController public class HelloController @RequestMapping("/hello") public String handle01 () return "Hello Spring Boot 2" ; } }
其中@RestController的作用等于@Controller + @ResponseBody
在resources目录下创建application.properties文件,在其内修改Spring Boot的配置属性
1 2 3 4 5 server.port =8080 server.servlet.context-path : /projectName
Springboot官方配置项文档
在maven的pom文件中添加插件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
对当前工程进行打包:
得到springboot-helloworld-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar后,直接在命令行运行:java -jar springboot-helloworld-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar即可启动整个工程。
在Spring 5版本之后,该注解添加了属性:proxyBeanMethods,该属性可用于两种模式:
Full模式(proxyBeanMethods = true):@Bean方法返回的组件是单实例的(默认)
Lite模式(proxyBeanMethods = false):@Bean方法返回的组件每次都是新创建 的。
proxyBeanMethods作用(经测试,在使用Spring基础框架创建配置类时该属性无效,均不返回代理对象):
proxyBeanMethods值为true时,@Configuration配置类中注册的所有组件都会被创建其代理对象并保存在容器中 。在配置类中写的所有组件注册方法在被外界调用时都会去容器中找是否已经存在该对象的代理对象 ,若存在则直接获取,若不存在则再创建代理对象 ,即单例模式。proxyBeanMethods值为false时,在容器中不会再保存代理对象,在外界调用该方法时都会产生新的对象(非代理对象)。
最佳实践:
配置类组件之间无依赖关系 用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
配置类组件之间有依赖关系 ,方法会在被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式(默认)
配置类MyConfig.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class MyConfig @Bean public User user () User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan" , 18 ); zhangsan.setPet(Pet()); return zhangsan; } @Bean("pet") public Pet Pet () return new Pet("gaolaoer" ); } }
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan("com.zhao.boot") public class MainApplication public static void main (String[] args) ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args); String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String name : names) { System.out.println(name); } Pet pet01 = run.getBean("pet" , Pet.class); Pet pet02 = run.getBean("pet" , Pet.class); System.out.println("组件:" +(pet01 == pet02)); MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class); System.out.println(bean); User user = bean.user(); User user1 = bean.user(); System.out.println(user == user1); User user2 = run.getBean("user" , User.class); Pet pet = run.getBean("pet" , Pet.class); System.out.println("用户的宠物:" +(user2.getPet() == pet)); } }
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入
使用@ImportResource可以导入其他Spring的xml文件,导入后该xml文件中的组件会被添加到当前配置类中,使用方法:
1 2 3 4 @ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml") public class MyConfig }
使用@ConfigurationProperties进行配置绑定,将配置文件中的属性值赋给某个组件。
创建application.properties文件,在其中添加属性值:
1 2 mycar.brand =BYD mycar.price =100000
给某个类添加@Component注解,将其注册到容器中(只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有Spring Boot提供的强大功能)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar") public class Car String brand; String price; }
之后该组件中的属性将在配置文件中寻找同名的key,将其对应的value赋给属性值。
@ConfigurationProperties注解在Spring Boot底层大量使用,使用其修饰的组件将从Spring Boot核心配置文件application.properties中读取并绑定相关配置参数。
Spring Boot另一种配置绑定方式:@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
@EnableConfigurationProperties的功能:
开启配置绑定功能(让其能够绑定到配置文件)
把组件自动注册到容器中(使其可以不写@Component注解也能注册到容器中)
1 2 3 4 @EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class) public class MyConfig }
1 2 3 4 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar") public class Car }
@Bean、@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Import,它们是Spring的基本标签,在Spring Boot中并未改变它们原来的功能。
当前新建的Spring Boot项目的父项目:
1 2 3 4 5 <parent > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4.RELEASE</version > </parent >
其父项目又依赖spring-boot-dependencies.pom:
1 2 3 4 5 <parent > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4.RELEASE</version > </parent >
该文件中声明了开发中常用的jar包版本,因此其子项目中不需要给依赖写上版本号,会自动导入父项目里版本的jar包。该特性被称为版本仲裁 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <properties > <activemq.version > 5.15.13</activemq.version > <antlr2.version > 2.7.7</antlr2.version > <appengine-sdk.version > 1.9.82</appengine-sdk.version > <artemis.version > 2.12.0</artemis.version > <aspectj.version > 1.9.6</aspectj.version > <assertj.version > 3.16.1</assertj.version > ... </properties >
若想自定义修改依赖的版本,则只需要在当前项目里指定配置版本号,其会覆盖父项目中的默认版本号。
1 2 3 <properties > <mysql.version > 5.1.43</mysql.version > </properties >
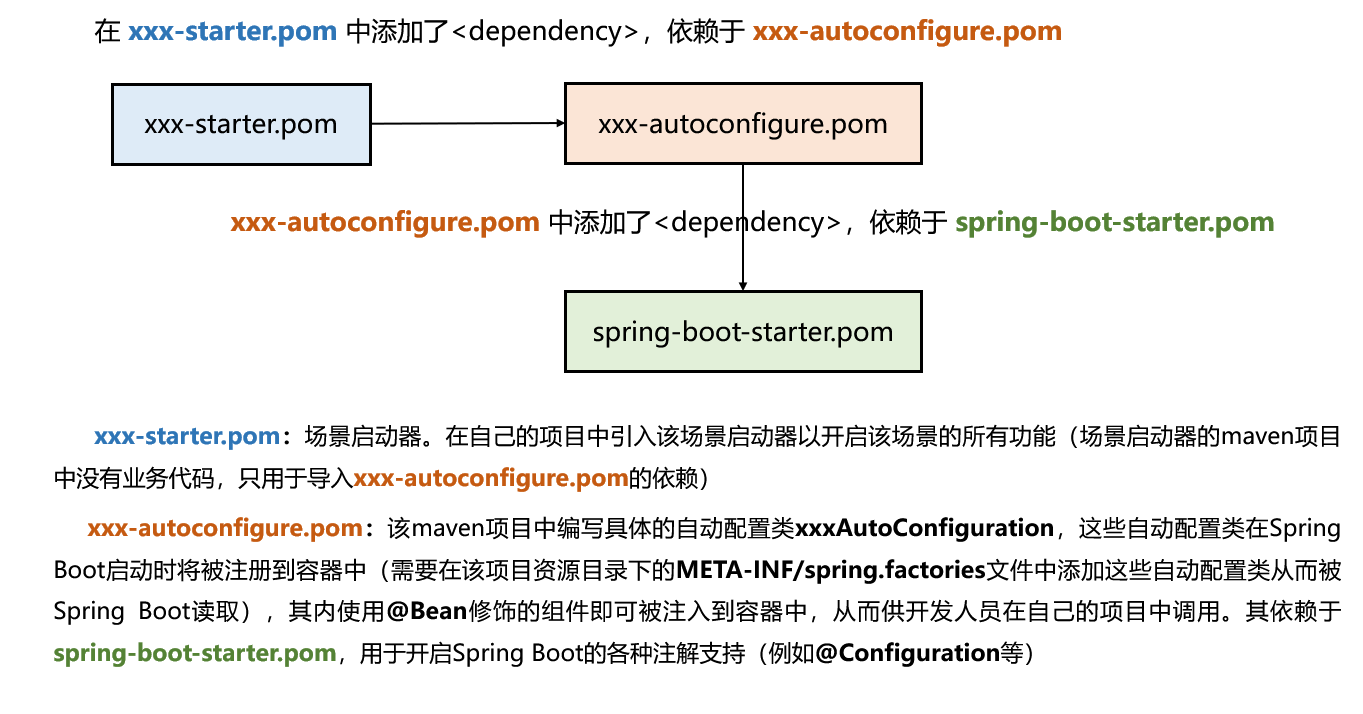
spring-boot-starter-* 代表某种场景,只要引入了该starter,这个场景的所有依赖都会自动引入。第三方提供的简化开发的场景启动器命名格式:*-spring-boot-starter。官方所有支持的Starter
所有场景启动器最底层的依赖,SpringBoot自动配置的核心依赖 :spring-boot-starter
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4.RELEASE</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency >
该starter场景将导入Spring Boot提供的127种自动配置类xxxAutoConfiguration ,这些自动配置类将导入许多常用的组件用于简化开发(例如DispatcherServlet等),无需开发人员手动添加这些组件。
spring-boot-starter.pom的主要内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xsi:schemaLocation ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" > <modelVersion > 4.0.0</modelVersion > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.5.3</version > <name > spring-boot-starter</name > <description > Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML</description > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot</artifactId > <version > 2.5.3</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId > <version > 2.5.3</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId > <version > 2.5.3</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > jakarta.annotation</groupId > <artifactId > jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId > <version > 1.3.5</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-core</artifactId > <version > 5.3.9</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.yaml</groupId > <artifactId > snakeyaml</artifactId > <version > 1.28</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency > </dependencies > </project >
场景启动器工作原理的本质:调用的xxx-starter项目导入的所有xxx-autoconfigure项目中编写了许多自动配置类xxxAutoConfiguration,这些自动配置类将在Spring Boot启动时被注册到容器中,从而将其内编写的组件按照条件注册到容器中,因此开发人员可以在自己的项目中调用到这些组件。
Spring Boot的主程序类(标有 @SpringBootApplication 注解的类)所在包及其下面的所有子包 里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来,这些组件不再需要额外指定扫描路径。而若想要扫描其他路径下的组件,则可以在主程序类上添加:
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.zhao.xxx")@ComponentScan("com.zhao.xxx")
@SpringBootApplication是一个合成注解,其效果等同于下面三个注解的组合。
1 2 3 @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan("com.zhao.xxx")
Spring Boot的各种配置都拥有默认值。这些默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:MultipartProperties。配置文件的值最终会绑定在某个类上,这个类会在容器中创建对象。
Spring Boot所有的自动配置功能 都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面。
@SpringBootApplication 是一个合成注解,其效果等同于下面三个注解的组合:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} ) public @interface SpringBootApplication
下面逐一分析上述三者的作用
表明被 @SpringBootApplication 修饰的类本质上也是一个 @Configuration 配置类
1 2 @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration
指定要扫描的组件(按照@Filter里设置的类型过滤一些组件)
重点,自动配置是通过该注解实现的。
1 2 3 @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration
3.1、@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包,将MainApplication主程序类所在包下的所有组件注册到容器中
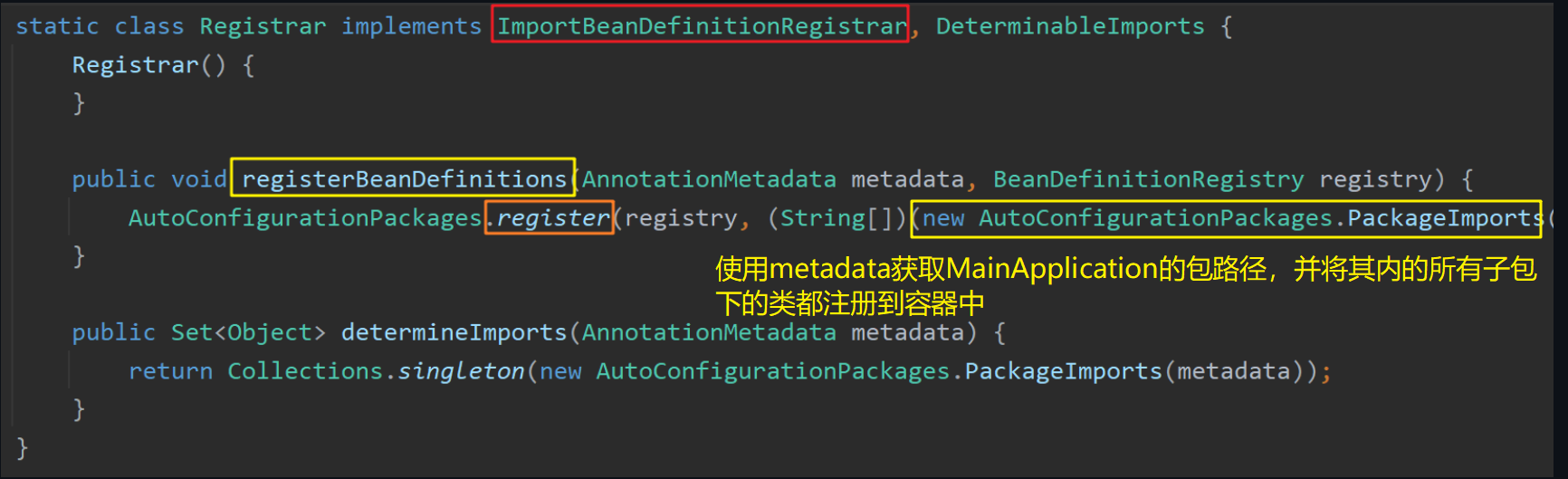
1 2 @Import({Registrar.class}) public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage
该注解通过@Import注解向容器中导入了一个Registrar 组件,该组件实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口(【Spring】Spring5 源码中常用接口的底层原理 将MainApplication主程序类所在包下的所有组件都注册到容器中 。这也解释了默认的扫描包路径为MainApplication所在包的路径。
其中传入的参数AnnotationMetadata metadata是指Spring Boot主程序类MainApplication的注解元信息,用于获取其所在的包路径,从而将该包下的所有子包下的类都注册到容器中。
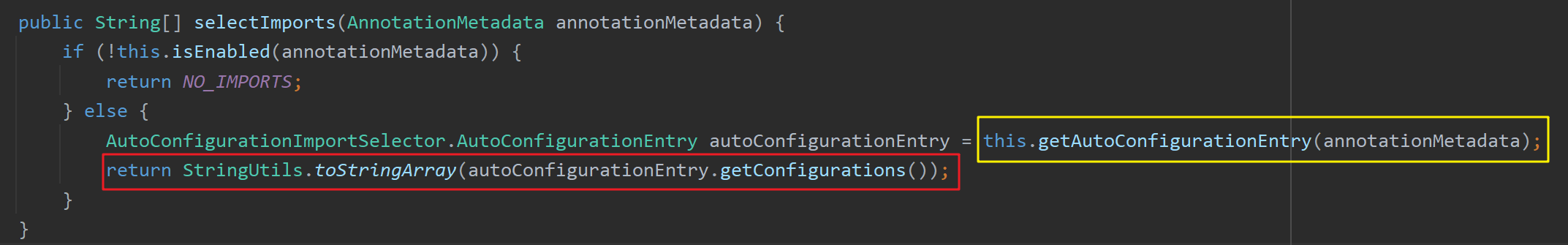
3.2、@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}):向容器中注册自动配置类
第一步:引导加载自动配置类
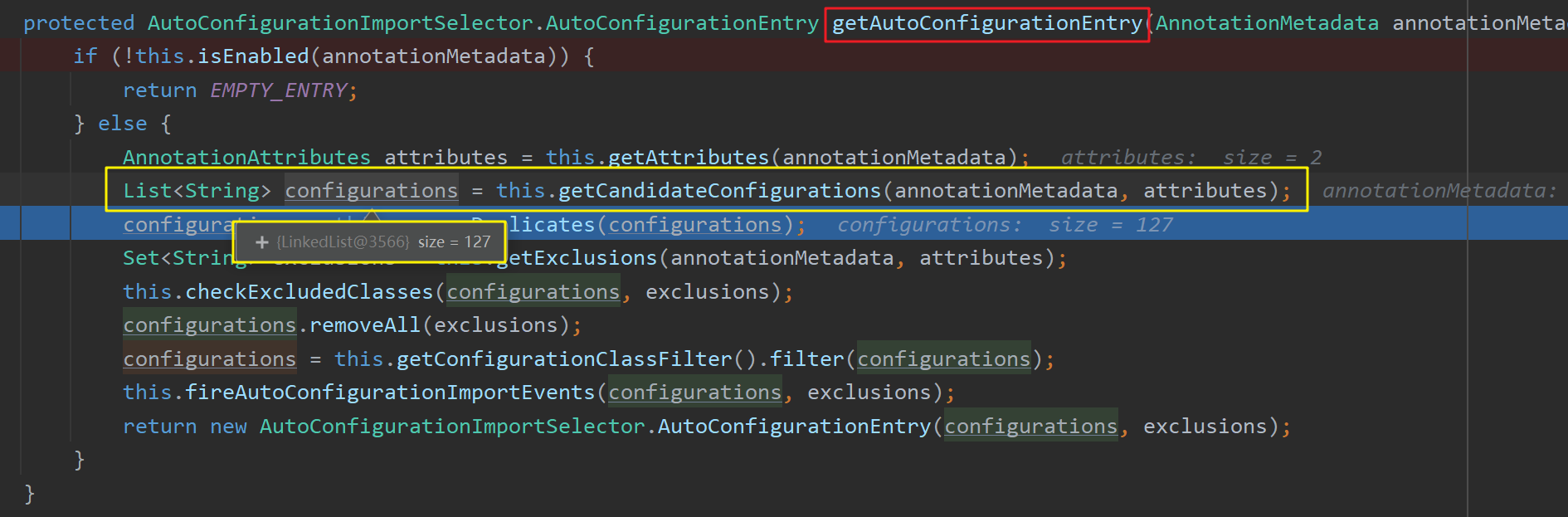
该注解向容器中注册了AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类型的组件,该类的重要方法 selectImports() 中利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata) 方法向容器中导入一些自动配置类 组件(先获取所有的自动配置类,再根据实际情况筛选出符合条件的自动配置类注册到容器中)。
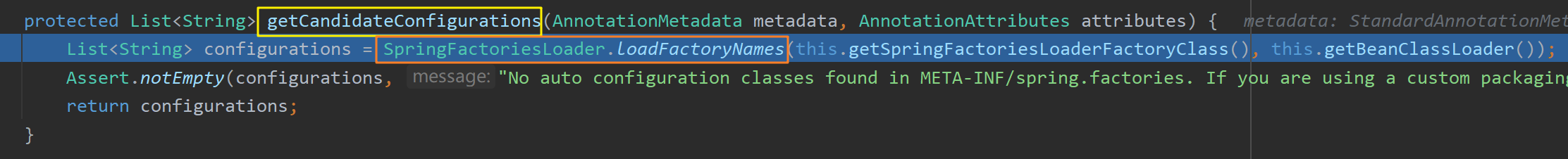
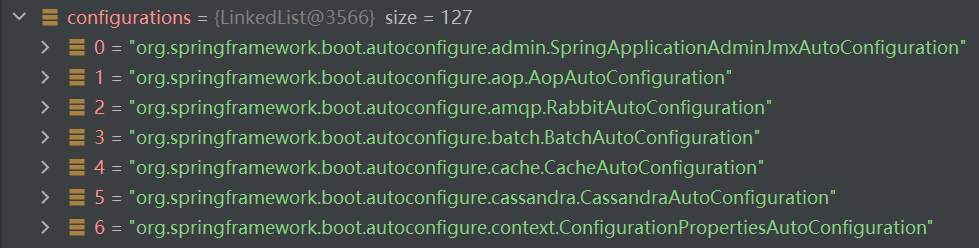
进入getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata)方法后,首先调用getCandidateConfigurations()方法获取所有候选 的自动配置类组件(AutoConfiguration),共有127个。并在后续进行删选后按需开启 自动配置项(即用不到的自动配置类无需开启)。
获取这些AutoConfiguration的具体过程:
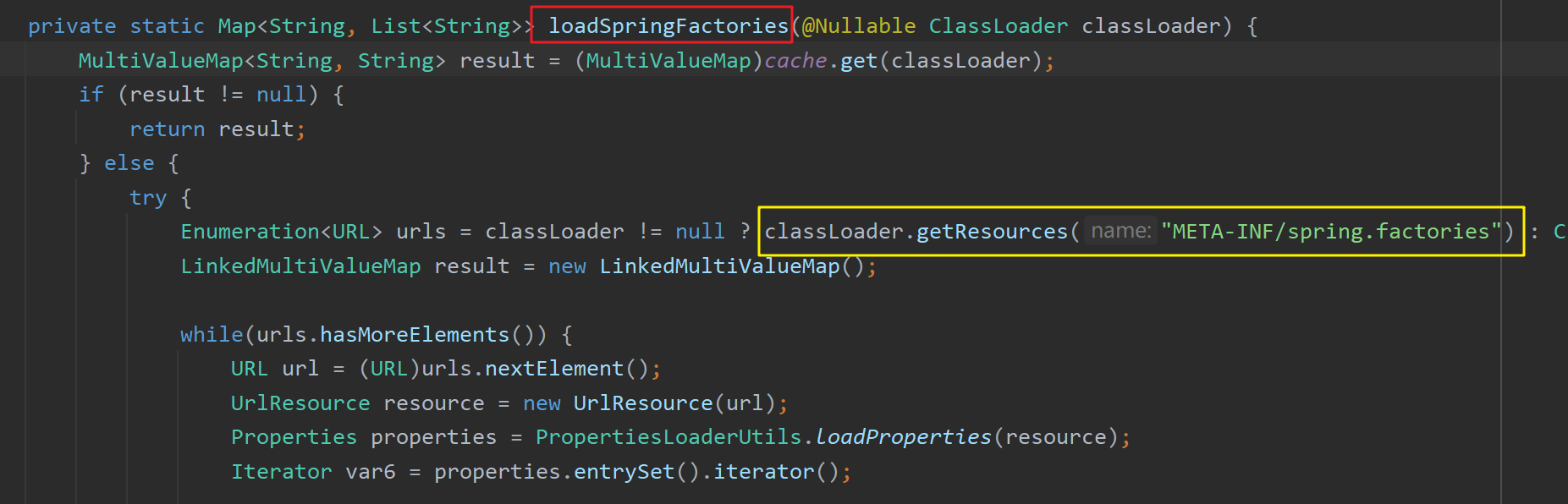
在getCandidateConfigurations()方法内通过SpringFactoriesLoader工厂加载器加载一些组件。
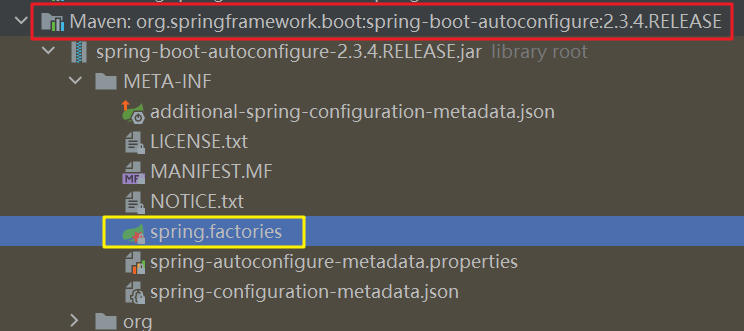
在该方法内使用类加载器读取"META-INF/spring.factories"位置处的资源文件。有些包下有这个文件,比如最关键的spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包(导入的其他第三方包中也可以会含有"META-INF/spring.factories"文件,例如MyBatis的mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.4.jar包也会有该文件,Spring Boot启动时也会加载该包下的xxxAutoConfiguration类):
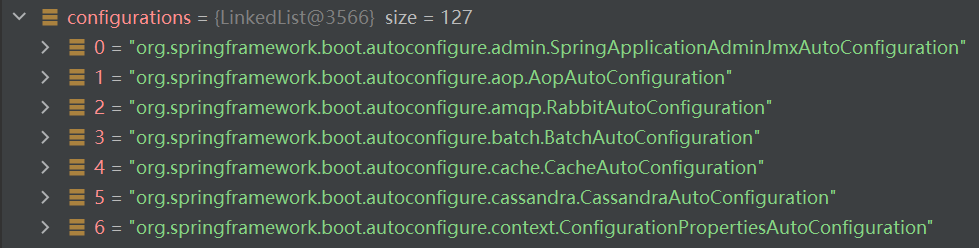
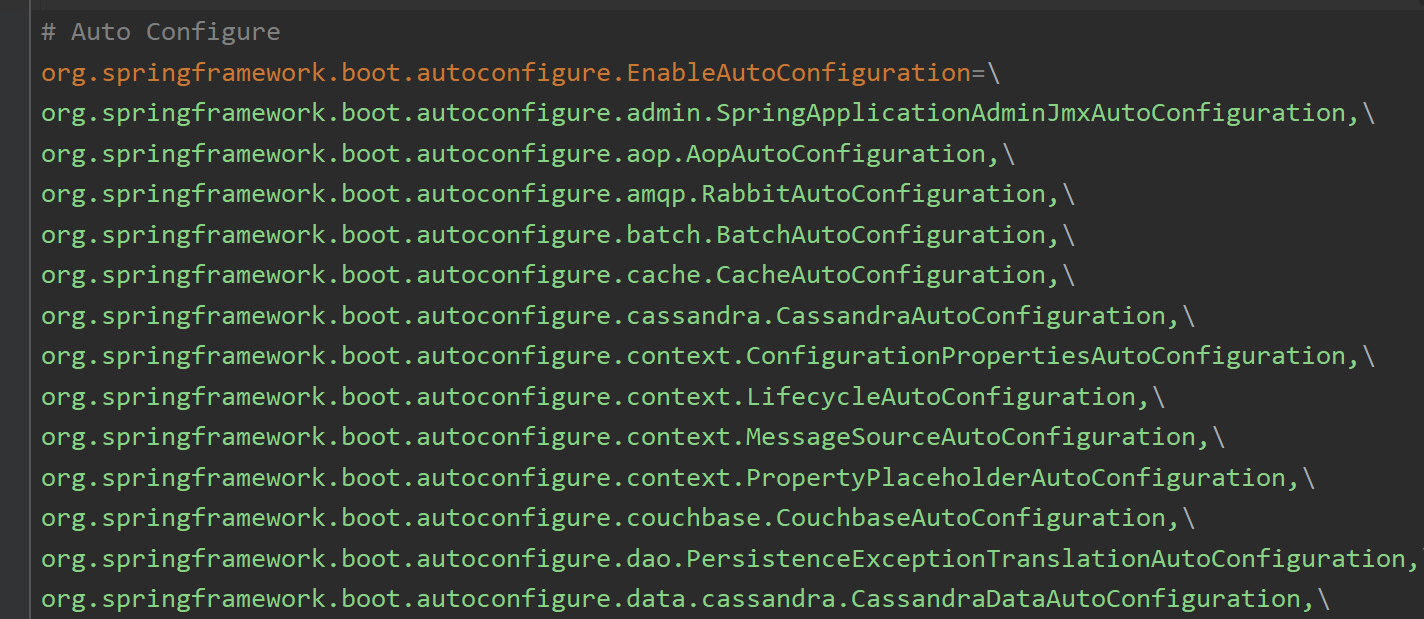
该文件内配置了Spring Boot启动时就要向容器中加载的所有自动配置类(AutoConfiguration)(共127个,正好对应上文中的127个自动配置类组件):
上文中注册到容器中的127个自动配置类组件Configurations:
但这127个自动配置类并不会都注册到容器中,而会按需开启。
第二步:按需开启自动配置项
虽然上述127个自动配置类在启动的时候会默认全部加载,但每个xxxxAutoConfiguration会按照条件装配规则(@Conditional )按需配置 。
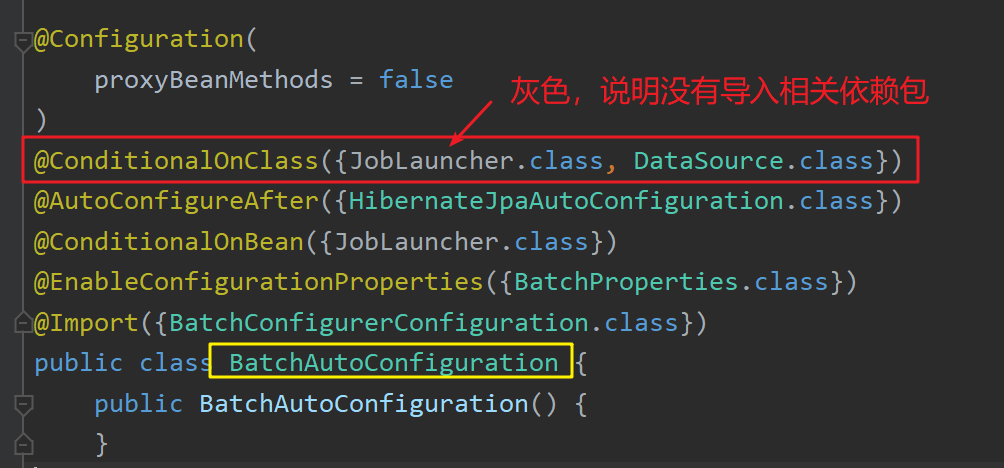
以BatchAutoConfiguration类为例,该类因@ConditionalOnClass({JobLauncher.class, DataSource.class})的存在,若想被注册到容器中,需要满足当前项目中有JobLauncher类的存在,但若开发人员没有导入该类相关的maven依赖,则无法找到该类,因此该自动配置类将不会被注册到容器中。因此上述127个自动配置类会按照实际容器中配置组件的情况按需注册到容器中,不需要的配置类将不会被注册。
同时这些自动配置类里的配置属性通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解从xxxProperties 组件中获取(xxxProperties组件和相应的配置文件绑定在了一起)
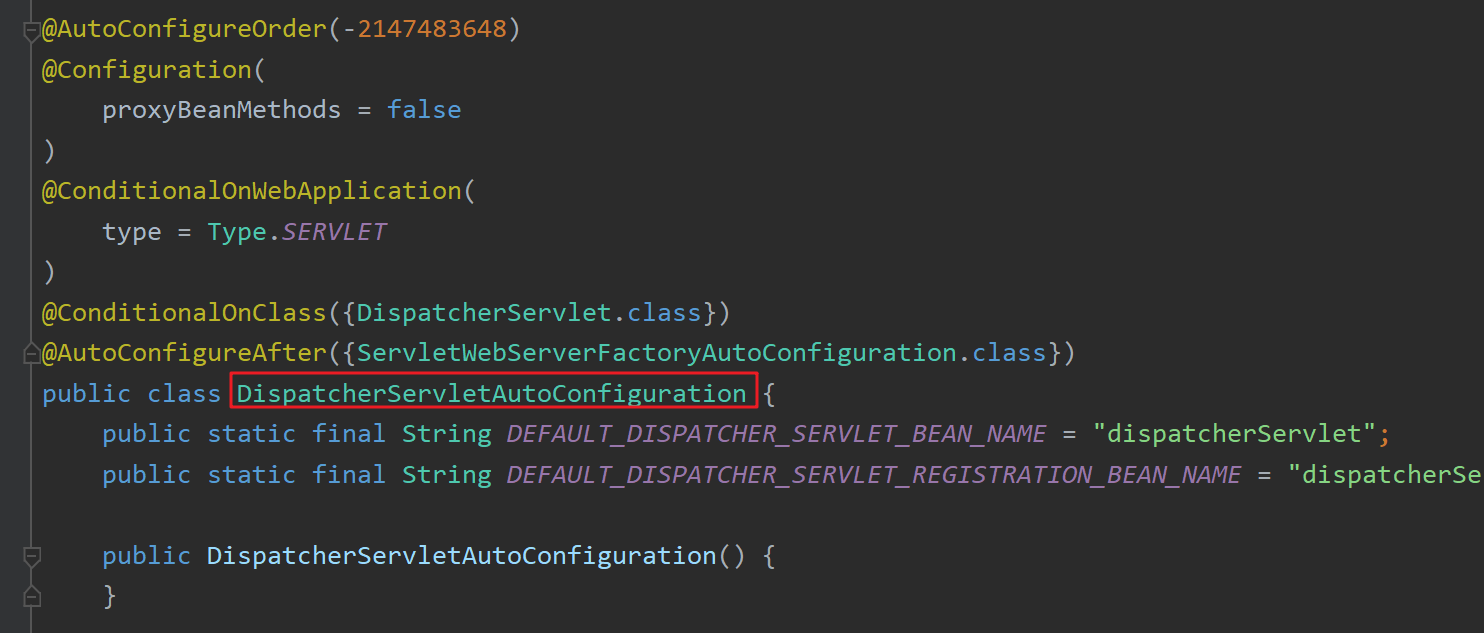
举例:上文描述了如何向容器中注册常用的自动配置类,下面以web开发必须的自动配置类DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration 为例:
该自动配置类满足@Conditional的条件,因此会在程序加载时被注册到容器中。同时该自动配置类中会向容器中注册DispatcherServlet 组件,这正是Spring MVC开发时需要的转发器组件。
也就是说Spring Boot在启动时,会将传统SSM中开发人员配置在xml中的必备组件自动地注册到容器中,无需开发人员再手动注册。
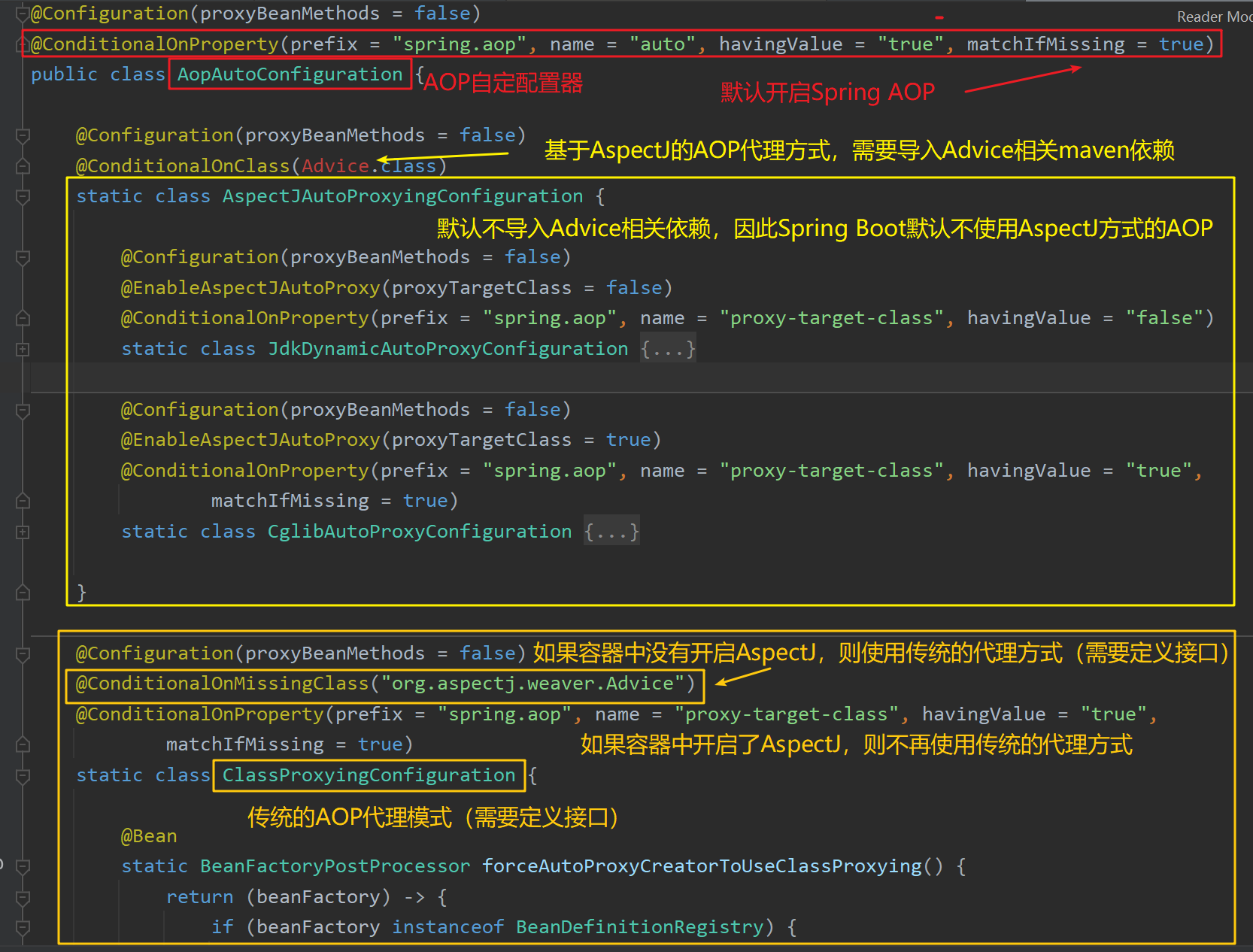
以AOP自动配置器AopAutoConfiguration 为例:
第三步:修改默认配置
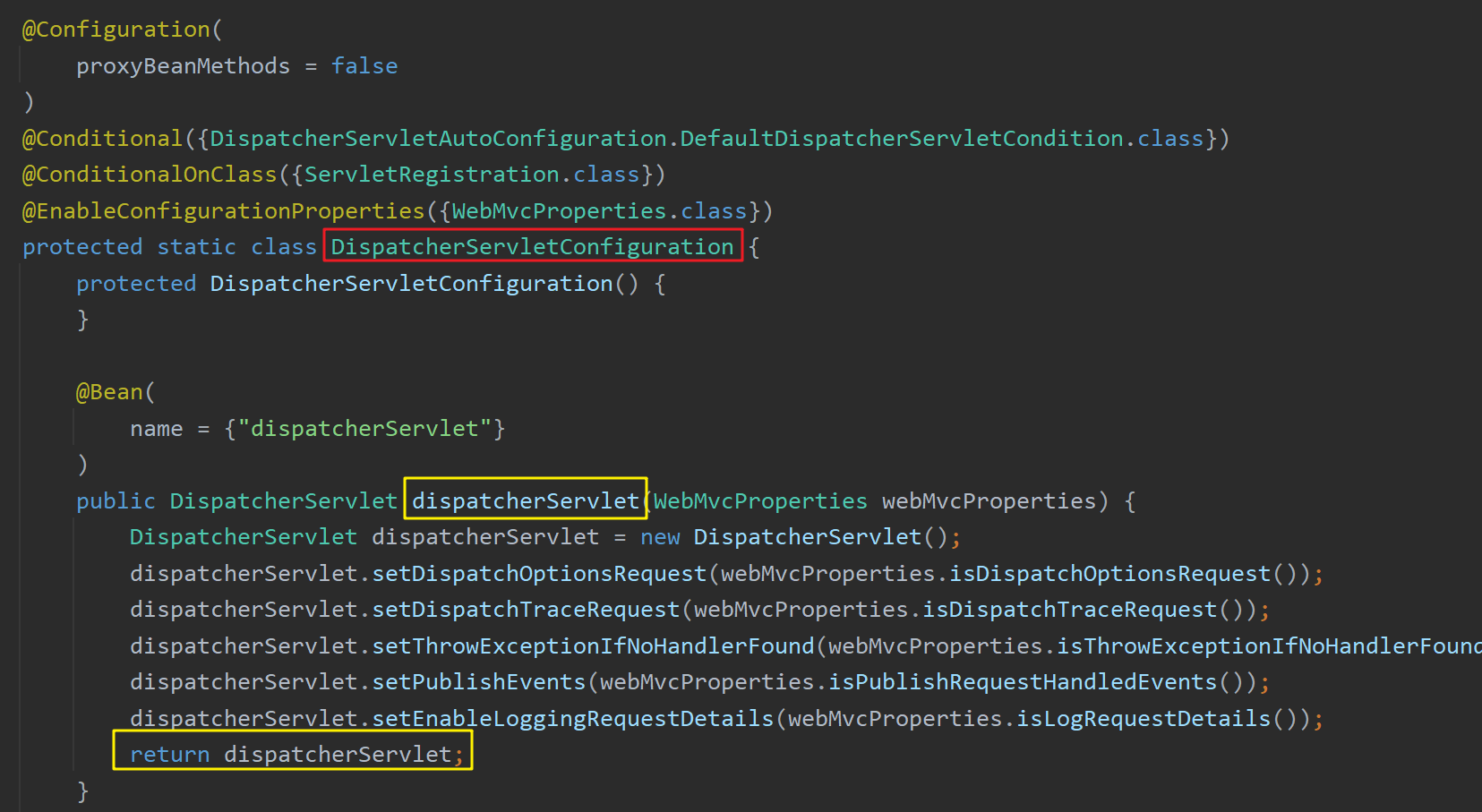
以自动配置类DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration 中的MultipartResolver 组件为例,该组件为Spring MVC中的文件上传组件,其会被DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration注册到容器中。
其依赖于MultipartResolver 组件(该组件默认存在于容器中,但开发人员可以再手动注册一个),同时判断该组件的名称是否为指定的MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = multipartResolver。
若不是,可能的情况为开发人员自己手动注册了一个,但名称不符合规范。此时容器通过调用multipartResolver()方法注册了该组件,同时注册的组件名就是方法名multipartResolver ,因此起到组件名规范化 的效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME) public MultipartResolver multipartResolver (MultipartResolver resolver) return resolver;
SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件。但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先:
1 2 3 4 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter () }
Spring Boot首先加载所有的自动配置类 xxxxxAutoConfiguration (127个)
每个自动配置类按照条件判断进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。(从xxxxProperties 组件里面读取,xxxProperties 组件和配置文件进行了绑定)
生效的配置类就会向容器中注册响应的组件
定制化配置:
开发人员手动使用@Bean替换容器中默认注册的组件;
在配置文件中修改相应配置属性以修改默认组件的属性值
xxxxxAutoConfiguration —> 注册组件 —> 组件属性通过 xxxxProperties 从配置文件application.properties 中取值
常用的自动配置类xxxAutoConfiguration :
AopAutoConfiguration :AOP自动配置类DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration :DispatcherServlet自动配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration :WebMVC相关自动配置类ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration :ServletWebServerFactory自动配置类MultipartAutoConfiguration :文件上传自动配置类ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration :异常处理自动配置类DataSourceAutoConfiguration :数据源自动配置类MybatisAutoConfiguration :MyBatis自动配置类(第三方)
Lombok用标签方式代替构造器、getter/setter()、toString()等代码。Spring Boot已经管理Lombok。引入依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency >
IDEA中File->Settings->Plugins,搜索安装Lombok插件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @NoArgsConstructor @Data @ToString @EqualsAndHashCode public class User private String name; private Integer age; private Pet pet; public User (String name,Integer age) this .name = name; this .age = age; } }
简化日志开发
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Slf4j @RestController public class HelloController @RequestMapping("/hello") public String handle01 (@RequestParam("name") String name) log.info("请求进来了...." ); return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!" +"你好:" +name; } }
添加依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > </dependencies >
在IDEA中,项目或者页面修改以后使用:Ctrl+F9更新。本质上是重新启动项目,并非真正的热部署。
Spring Initailizr New -> Project -> Spring Initailizr快速构建Spring Boot项目。
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)。其非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件 。
key: value;kv之间有空格
大小写敏感
使用缩进表示层级关系
缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
'#'表示注释
字符串无需加引号,如果要加,单引号’’、双引号""表示字符串内容会被 转义、不转义
字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 k: {k1:v1 ,k2:v2 ,k3:v3 }k: k1: v1 k2: v2 k3: v3
数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 k: [v1 ,v2 ,v3 ]k: - v1 - v2 - v3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Data public class Person private String userName; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Integer age; private Pet pet; private String[] interests; private List<String> animal; private Map<String, Object> score; private Set<Double> salarys; private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets; } @Data public class Pet private String name; private Double weight; }
用yaml表示以上对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 person: userName: zhangsan boss: false birth: 2019 /12/12 20 :12:33 age: 18 pet: name: tomcat weight: 23.4 interests: [篮球 ,游泳 ] animal: - jerry - mario score: english: first: 30 second: 40 third: 50 math: [131 ,140 ,148 ] chinese: {first: 128 ,second: 136 } salarys: [3999 ,4999.98 ,5999.99 ] allPets: sick: - {name: tom } - {name: jerry ,weight: 47 } health: [{name: mario ,weight: 47 }]
自定义的类和配置文件绑定一般没有提示。若要提示,添加如下依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <excludes > <exclude > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId > </exclude > </excludes > </configuration > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
Spring Boot为Spring MVC开发提供了大量的自动配置,无需开发人员再手动定义。默认配置如下:
内容协商视图解析器ContentNegotiatingViewResolver和组件名视图解析器BeanNameViewResolver
静态资源(包括webjars)
自动注册 Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter
支持消息转换器HttpMessageConverters
自动注册 MessageCodesResolver(国际化用)
静态 index.html 页支持
自定义 Favicon
自动使用 ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(DataBinder负责将请求数据绑定到JavaBean上)
若开发人员想要实现自定义的配置,则可以有三种方式:
使用 @Configuration + WebMvcConfigurer 自定义规则,同时不能标注 @EnableWebMvc 注解(若开启,则变成全面接管Spring MVC,就需要把所有Spring MVC配置好的规则全部自定义实现)
声明 WebMvcRegistrations 改变默认底层组件
使用 @EnableWebMvc+@Configuration+DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration ==全面接管 ==Spring MVC【详细源码分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
若想在容器中添加Spring MVC相关的自定义组件 以覆盖默认组件,则可以在**@Configuration中添加一个 WebMvcConfigurer组件,在其内 重写相关方法**即可覆盖容器中默认的方法。示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 @Configuration public class myConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()) .addPathPatterns("/**" ) .excludePathPatterns("/" ,"/login" ,"/css/**" ,"/fonts/**" ,"/images/**" ,"/js/**" ); } @Override public void addFormatters (FormatterRegistry registry) registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Person>() { @Override public Person convert (String s) Person person = new Person(); return person; } }); } @Override public void extendMessageConverters (List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) converters.add(new MyMessageConverter()); } @Override public void configureContentNegotiation (ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) Map<String, MediaType> mediaTypes = new HashMap<>(); mediaTypes.put("json" , MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); mediaTypes.put("xml" , MediaType.APPLICATION_XML); mediaTypes.put("myFormat" , MediaType.parseMediaType("application/x-zhao" )); ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy parameterStrategy = new ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy(mediaTypes); HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy headerStrategy = new HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy(); configurer.strategies(Arrays.asList(parameterStrategy, headerStrategy)); } }
只要静态资源放在类路径下的:/static (or/public or/resources or /META-INF/resources)目录,就可以通过 “当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名 ” 的方式访问到。原理: 静态映射 /**。
收到请求后,先去找Controller看能不能处理;不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器 ;静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
默认的静态资源路径可以通过修改"static-locations"属性值来定制化:
1 2 resources: static-locations: [classpath:/myStaticPath/ ]
此时,浏览器在访问"static-locations“目录下的静态资源文件时,解析得到的请求路径不包含”static-locations"。例如:访问"/static/css/style.css“时,解析到的请求路径是”/css/style.css "。
详细源码分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
当前项目名称 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名 = 去static-locations属性配置的静态资源文件夹下找"静态资源名"文件
1 2 3 spring: mvc: static-path-pattern: /res/**
注意:配置了前缀后,就不能使用欢迎页功能了。
通过配置add-mappings属性可以禁止所有静态资源规则。
1 2 3 spring: resources: add-mappings: false
可用jar方式添加css,js等资源文件,https://www.webjars.org/。
例如,添加jquery:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > jquery</artifactId > <version > 3.5.1</version > </dependency >
访问地址:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js 后面地址要按照依赖里面的包路径。
Spring Boot 只支持自动跳转到 index.html 页面。templates 目录下的其他路径都不能直接在浏览器中访问到,必须通过 Controller 进行跳转
在静态资源路径下创建 index.html 文件,其会被设置为欢迎页。可以自定义配置静态资源路径 以在任意位置存放该文件,但注意不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀 ,否则导致 index.html 不能被默认访问。controller能处理 /index 。
1 2 3 4 5 spring: resources: static-locations: [classpath:/myPath/ ]
指网页标签上的小图标。favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可。但注意配置静态资源的访问前缀 将导致Favicon功能失效
实现Rest风格支持的核心Filter:HiddenHttpMethodFilter 。其本质是一个过滤器,因此会在所有请求响应前进行拦截过滤,将DELETE请求和PUT请求进行包装后放行到后续过滤器。
1 2 3 4 5 spring: mvc: hiddenmethod: filter: enabled: true
开启HiddenHttpMethodFilter 后,若想发送DELETE或PUT请求,则需要创建一个表单,在表单项中携带一个_method参数,这个参数的值可以设置为DELETE或PUT。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <form action ="/user" method ="get" > <input value ="REST-GET提交" type ="submit" /> </form > <form action ="/user" method ="post" > <input value ="REST-POST提交" type ="submit" /> </form > <form action ="/user" method ="post" > <input name ="_method" type ="hidden" value ="DELETE" /> <input value ="REST-DELETE 提交" type ="submit" /> </form > <form action ="/user" method ="post" > <input name ="_method" type ="hidden" value ="PUT" /> <input value ="REST-PUT提交" type ="submit" /> <form >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @GetMapping("/user") public String getUser () return "GET-张三" ; } @PostMapping("/user") public String saveUser () return "POST-张三" ; } @PutMapping("/user") public String putUser () return "PUT-张三" ; } @DeleteMapping("/user") public String deleteUser () return "DELETE-张三" ; }
HiddenHttpMethodFilter 的源码分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
@PathVariable :路径变量@RequestHeader :获取请求头@RequestParam :获取请求参数(指问号后的参数,url?a=1&b=2)@CookieValue :获取Cookie值@RequestAttribute :获取request域属性@RequestBody :获取请求体[POST]@MatrixVariable :矩阵变量
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 @RestController public class ParameterTestController @GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}") public Map<String,Object> getCar (@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String name, @PathVariable Map<String,String> pv, @RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent, @RequestHeader Map<String,String> header, @RequestParam("age") Integer age, @RequestParam("inters") List<String> inters, @RequestParam Map<String,String> params, @CookieValue("_ga") String _ga, @CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie) Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("age" ,age); map.put("inters" ,inters); map.put("params" ,params); map.put("_ga" ,_ga); System.out.println(cookie.getName()+"===>" +cookie.getValue()); return map; } @PostMapping("/save") public Map postMethod (@RequestBody String content) Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("content" ,content); return map; } @GetMapping("/goto") public String goToPage (HttpServletRequest request) request.setAttribute("msg" ,"成功了..." ); request.setAttribute("code" ,200 ); return "forward:/success" ; } @GetMapping("/params") public String testParam (Map<String,Object> map, Model model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) map.put("hello" ,"world666" ); model.addAttribute("world" ,"hello666" ); request.setAttribute("message" ,"HelloWorld" ); Cookie cookie = new Cookie("c1" ,"v1" ); response.addCookie(cookie); return "forward:/success" ; } @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/success") public Map success (@RequestAttribute(value = "msg", required = false) String msg, @RequestAttribute(value = "code", required = false) Integer code, HttpServletRequest request, RedirectAttributes ra) Object msg1 = request.getAttribute("msg" ); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Object hello = request.getAttribute("hello" ); Object world = request.getAttribute("world" ); Object message = request.getAttribute("message" ); map.put("reqMethod_msg" ,msg1); map.put("annotation_msg" ,msg); map.put("hello" ,hello); map.put("world" ,world); map.put("message" ,message); return map; } }
@MatrixVariable 与UrlPathHelper
@MatrixVariable 请求路径格式:/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd。示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @RestController public class ParameterTestController @GetMapping("/cars/{path}") public Map carsSell (@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low, @MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand, @PathVariable("path") String path) Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("low" ,low); map.put("brand" ,brand); map.put("path" ,path); return map; } @GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}") public Map boss (@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge, @MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge) Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("bossAge" ,bossAge); map.put("empAge" ,empAge); return map; } }
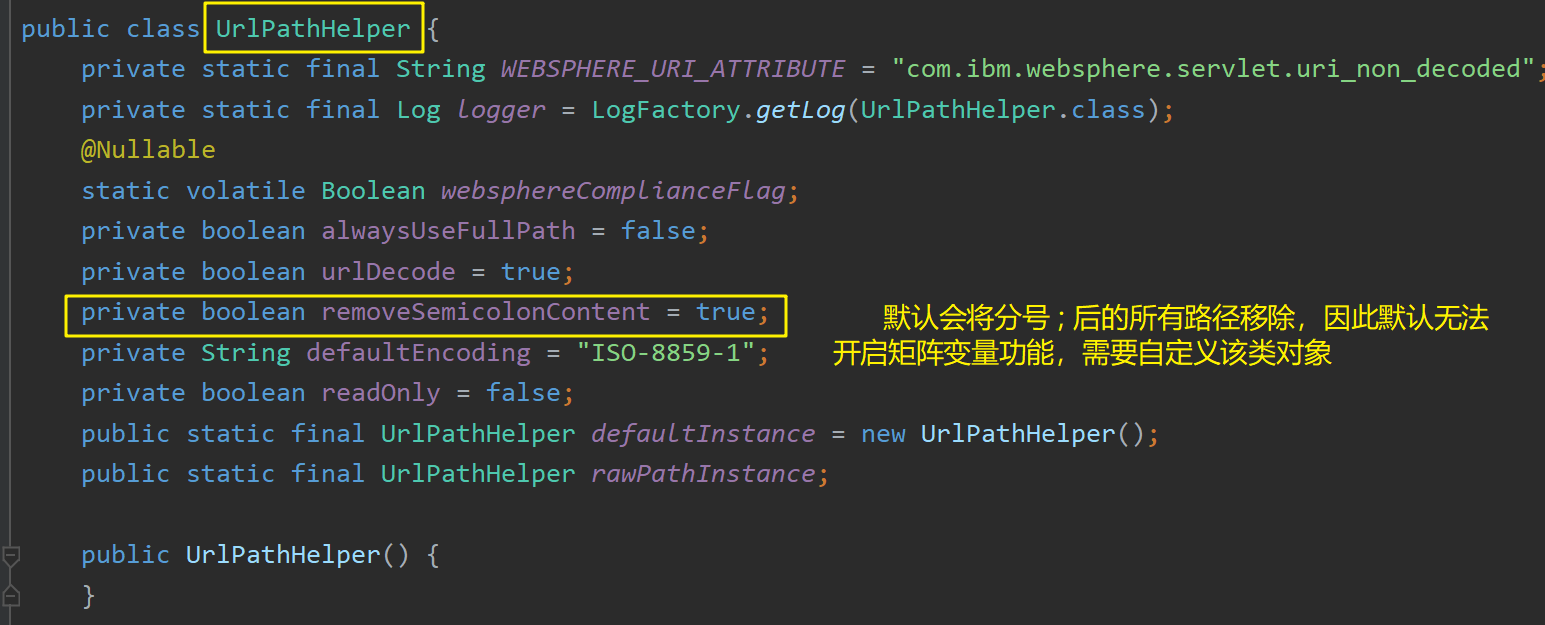
Spring Boot 默认是禁用了 矩阵变量的功能。若想手动开启,需要自定义一个WebMvcConfigurer 配置器的实现类,在其中将UrlPathHelper 的属性removeSemicolonContent 设置为false,让其支持矩阵变量的。具体做法:
方法一:实现WebMvcConfigurer 接口,令其代替**@EnableWebMvc**注解,实现定制的配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void configurePathMatch (PathMatchConfigurer configurer) UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false ); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } }
方法二:在容器中注入一个WebMvcConfigurer组件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class WebConfig @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer () return new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void configurePathMatch (PathMatchConfigurer configurer) UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false ); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } } } }
原理分析:
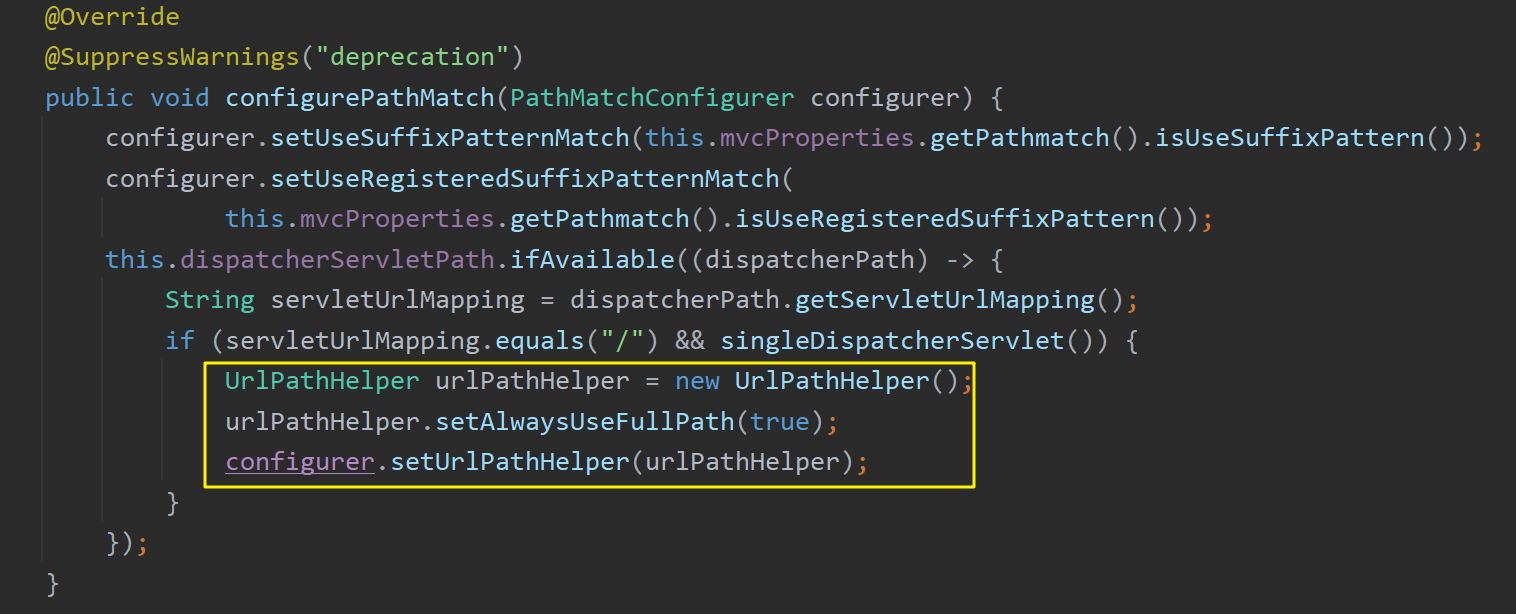
WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 类实现了WebMvcConfigurer 接口,其中有configurePathMatch()方法,该方法将创建一个 UrlPathHelper 类对象用于解析url。
默认创建的UrlPathHelper 类对象会将分号 ; 后的所有路径移除,因此默认配置下无法开启矩阵变量功能,需要重写WebMvcConfigurer 接口的configurePathMatch()方法,自定义一个 UrlPathHelper 对象,并将removeSemicolonContent 属性设置为false:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void configurePathMatch (PathMatchConfigurer configurer) UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false ); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } }
面试题:Filter 和 Interceptor 几乎拥有相同的功能,二者有何区别?
Filter 是 Servlet 定义的原生组件,好处是可以脱离 Spring 应用也能使用;其工作时机早于 Interceptor,在请求映射前执行。不符合过滤器的请求将被丢弃,不会经过拦截器 Interceptor 是 Spring 定义的接口,可以使用 Spring 的自动装配等功能
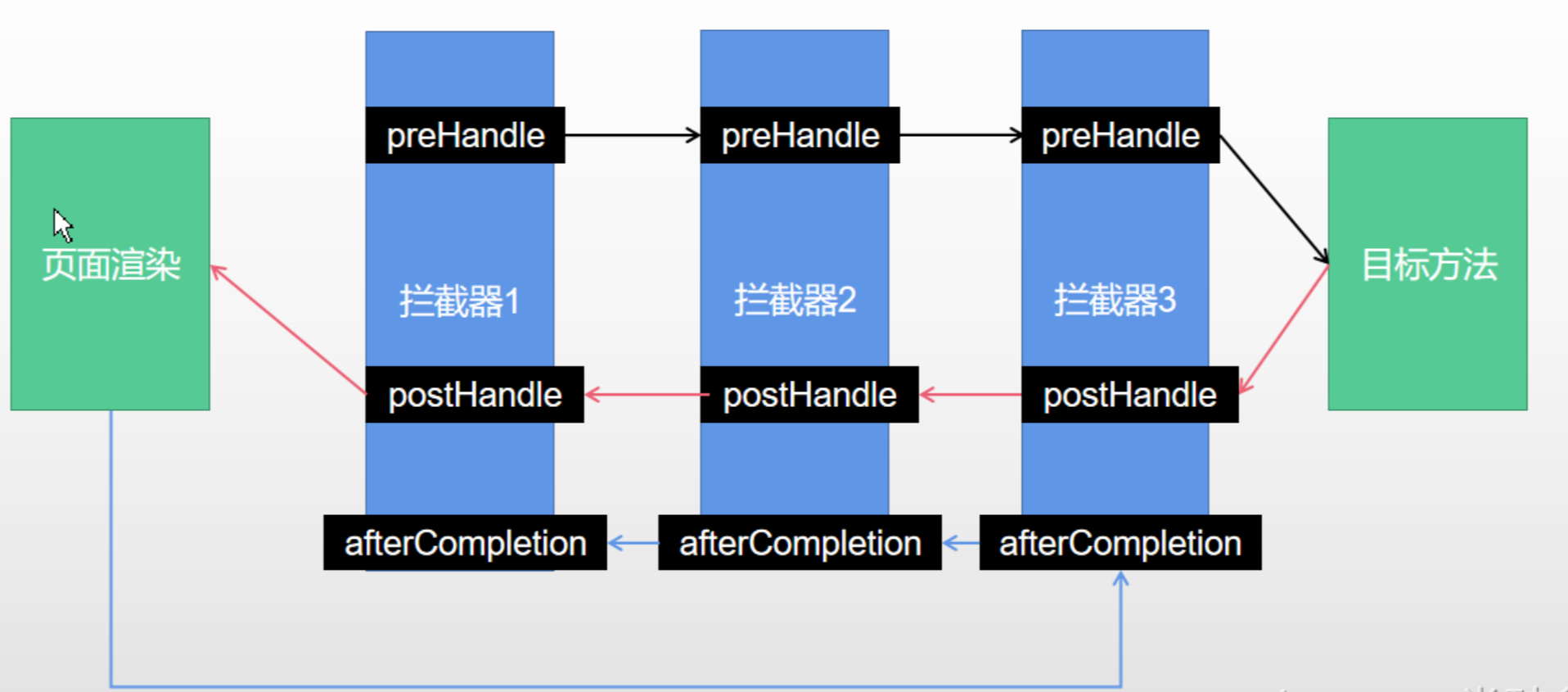
过滤器和拦截器的执行时机 :过滤前处理 - 拦截前处理 - 目标方法执行 - 拦截后处理 - 过滤后处理
所有拦截器都实现了HandlerInterceptor 接口,要想自定义拦截器,需要以下步骤:
编写一个拦截器实现HandlerInterceptor 接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @Slf4j public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception log.info("拦截的请求路径是" + request.getRequestURI()); HttpSession session = request.getSession(); Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser" ); if (loginUser!=null ){ return true ; } request.setAttribute("msg" , "请先登录" ); request.getRequestDispatcher("/" ).forward(request, response); return false ; } @Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception } @Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception } }
将拦截器注册到容器中(实现WebMvcConfigurer 接口的 addInterceptors() 方法)
指定拦截规则(如果设置路径为"/**",则静态资源也会被拦截)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()) .addPathPatterns("/**" ) .excludePathPatterns("/" ,"/login" ,"/css/**" ,"/fonts/**" ,"/images/**" ,"/js/**" ); } }
拦截器方法的执行在DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch(request, response) 方法栈中,大致流程为:
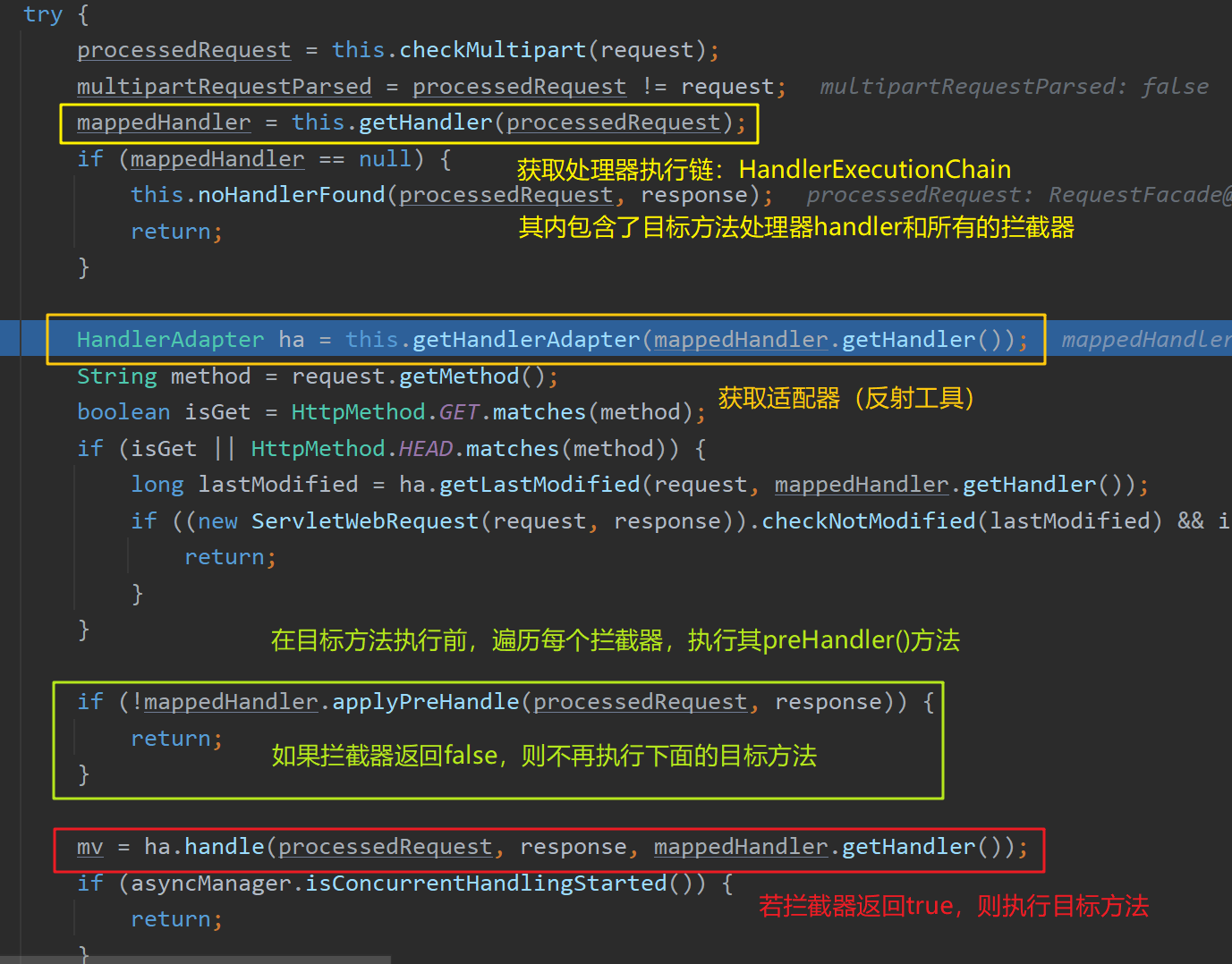
根据当前url请求,获取到目标方法对应的处理器执行链HandlerExecutionChain ,其内包含了目标方法处理器handler 以及容器中所有的拦截器interceptorList
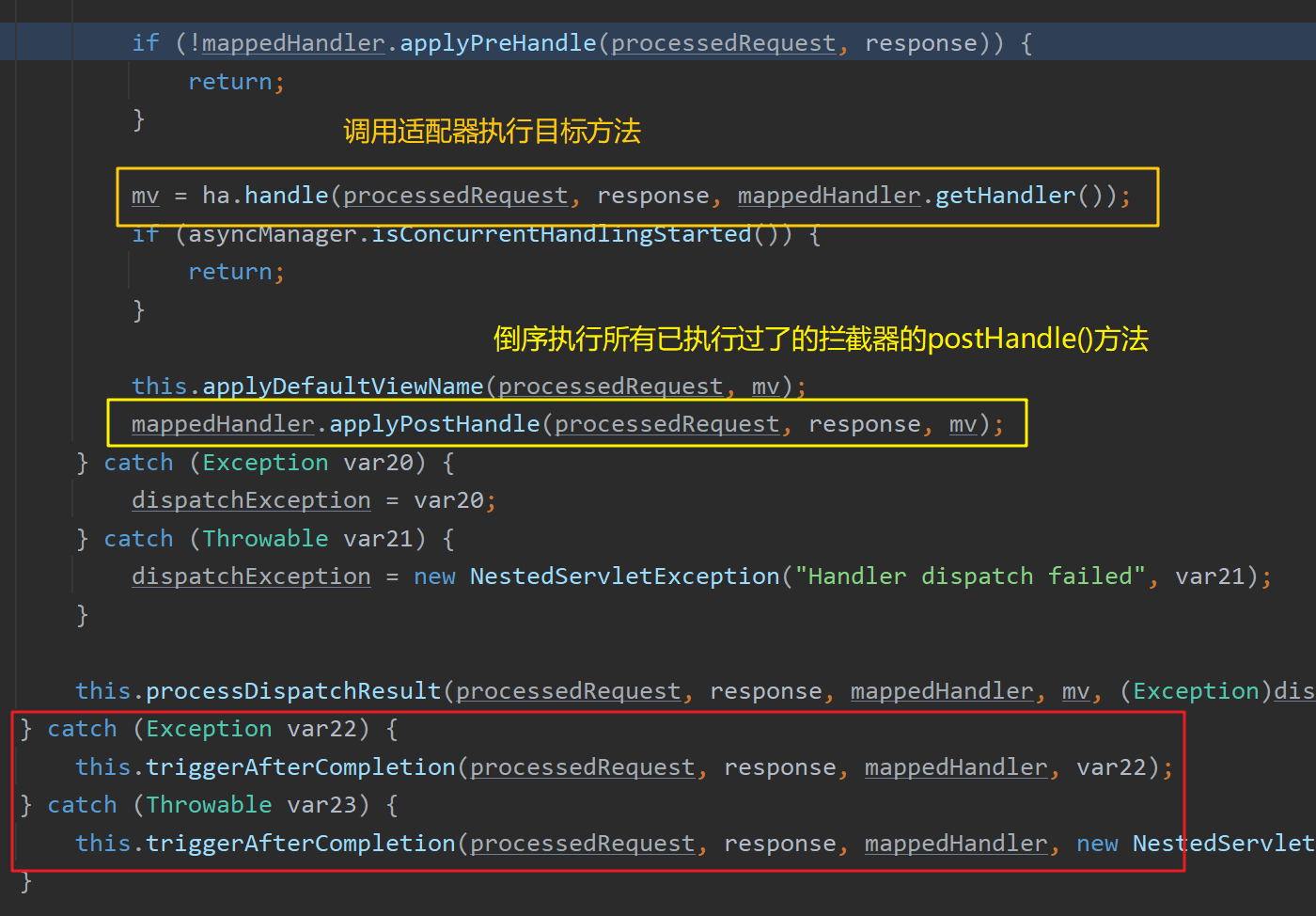
在目标方法执行前,调用 mappedHandler.applyPreHandle() 方法顺序 遍历容器中的所有拦截器,依次执行其 preHandle() 方法:
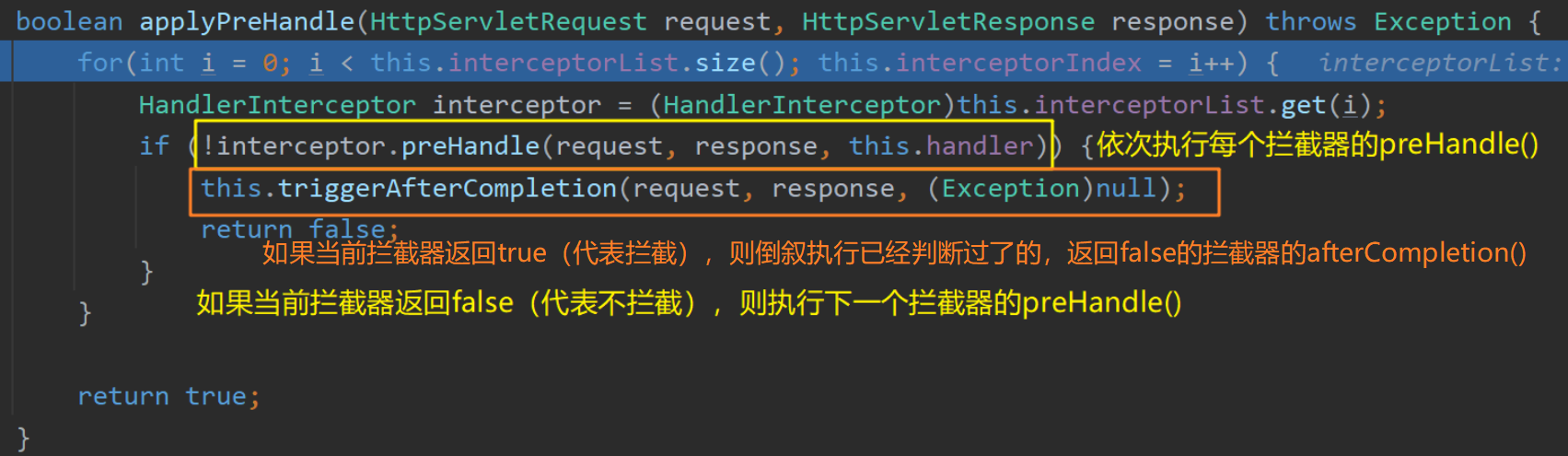
如果当前遍历到的拦截器的 preHandle() 方法返回true,则执行下一个拦截器的 preHandle() 方法
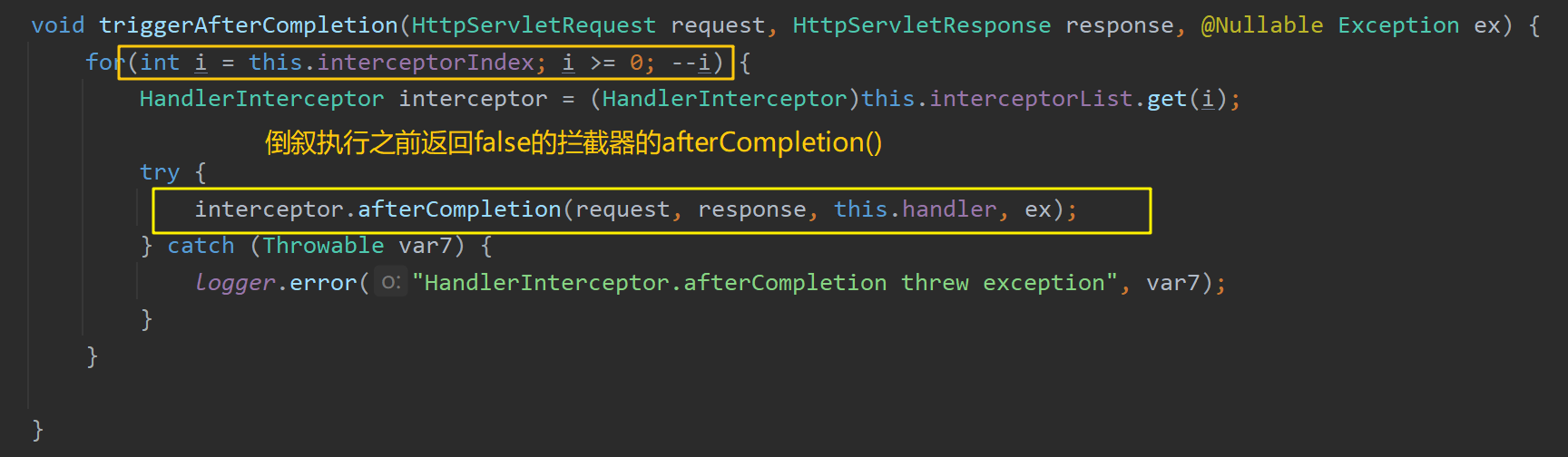
如果当前拦截器返回false,则倒序 执行所有已执行过了的拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
如果任意一个拦截器返回了false,则 doDispatch(request, response) 方法直接return,不再向下执行目标方法等代码
如果所有拦截器都返回true,则继续向下执行目标方法等代码
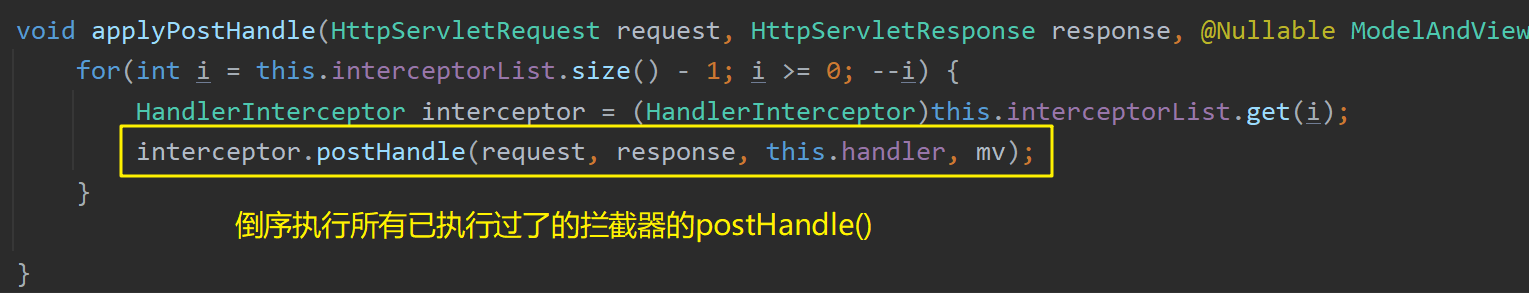
调用 ha.handle() 方法执行完目标方法后调用 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle() 方法倒序 执行所有已执行过了的拦截器的 postHandle() 方法
页面成功渲染后( processDispatchResult() 方法内),倒序 执行所有已执行过了的拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
之前步骤中有任何地方发生异常都会倒序 执行所有已执行过了的拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
上述流程截图:
之后补充reiggerAfter 和 processDispatchResult()的注释
放到Spring Boot源码
拦截器链的执行顺序:
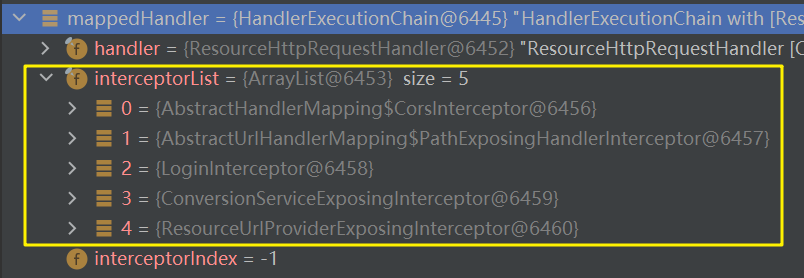
返回的mappedHandler 即处理器执行链HandlerExecutionChain ,其内包含了目标方法处理器handler 以及容器中所有的拦截器interceptorList ,其内包含了自定义的拦截器:
mappedHandler.applyPreHandle() 方法内顺序遍历容器中的所有拦截器,依次执行其 preHandle() 方法:
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle() 方法内倒序执行所有已执行过了的拦截器的 postHandle() 方法:
afterCompletion() 方法的触发时机:
目标方法执行前,遍历所有拦截器,执行其preHandle()方法,若某个拦截器该方法返回false,则倒序执行所有在该拦截器之前执行的(即在之前判断过的,拦截器返回true的)拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
页面渲染完成之前的所有步骤有任何地方出现异常,就会倒序触发所有已执行过的拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
页面成功渲染之后,倒序触发所有已执行过的拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法
在Spring Boot中实现文件上传功能的步骤:
在html文件中配置表单信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <form role ="form" th:action ="@{/upload}" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > <div class ="form-group" > <label for ="exampleInputEmail1" > 邮箱</label > <input type ="email" name ="email" class ="form-control" id ="exampleInputEmail1" placeholder ="Enter email" > </div > <div class ="form-group" > <label for ="exampleInputPassword1" > 名字</label > <input type ="password" name ="userName" class ="form-control" id ="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder ="Password" > </div > <div class ="form-group" > <label for ="exampleInputFile" > 头像</label > <input type ="file" name ="headerImg" id ="exampleInputFile" > </div > <div class ="form-group" > <label for ="exampleInputFile2" > 生活照</label > <input type ="file" name ="photos" id ="photos" multiple > </div > <button type ="submit" class ="btn btn-primary" > 提交</button > </form >
添加相应的处理方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @PostMapping("/upload") public String upload (@RequestParam("email") String email, @RequestParam("userName") String userName, @RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headerImg, @RequestPart("photos") MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException log.info("上传的信息:email={}, userName={}, headerImg={}, photos={}" , email, userName, headerImg.getSize(), photos.length); if (!headerImg.isEmpty()) { String originalFilename = headerImg.getOriginalFilename(); headerImg.transferTo(new File("D:/cache/" + originalFilename)); } if (photos.length > 0 ){ for (MultipartFile photo : photos) { String originalFilename = photo.getOriginalFilename(); photo.transferTo(new File("D:/cache/" + originalFilename)); } } return "main" ; }
在配置文件中修改上传文件大小等属性:
1 2 spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size =10MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size =100MB
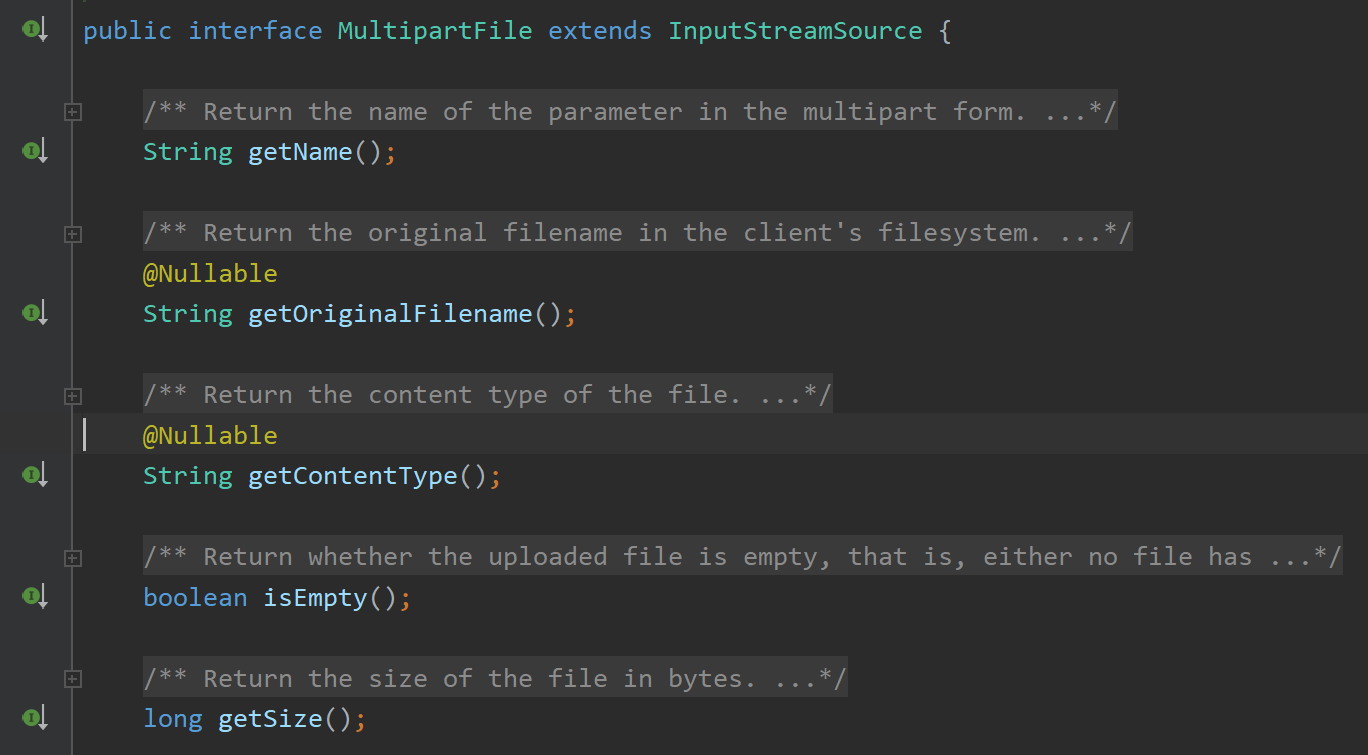
上述代码中解析得到的文件类型MultipartFile :
默认情况下,Spring Boot提供/error处理所有错误的映射。
对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。
对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据
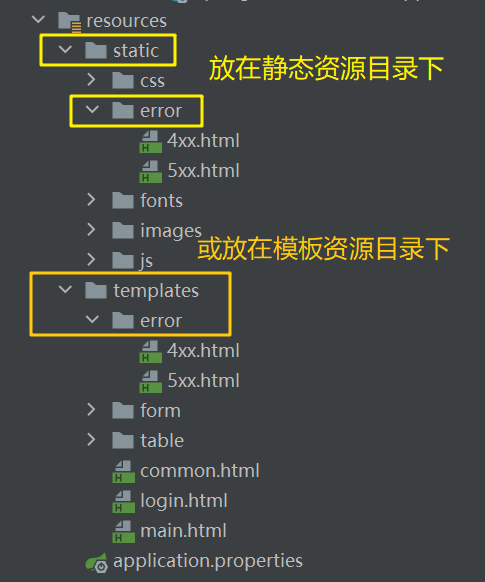
放在静态资源目录下的error/目录下的 4xx.html ,5xx.html 页面会被Spring Boot自动解析,作为错误页面展示在浏览器中:
@ServletComponentScan(basePackages=“com.zhao.admin”) :指定原生Servlet组件的存放路径。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zhao.admin") @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootWebAdminApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(SpringbootWebAdminApplication.class, args); } }
注入Servlet :注入的这些请求直接响应,没有被拦截器所拦截(原理分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/my") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException resp.getWriter().write("This is MyServlet" ); } }
注入Filter :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/css/*", "/images/*"}) public class MyFilter implements Filter @Override public void init (FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException } @Override public void doFilter (ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } @Override public void destroy () } }
注入Listener :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @WebListener public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener @Override public void contextInitialized (ServletContextEvent sce) } @Override public void contextDestroyed (ServletContextEvent sce) } }
在容器中注册的xxxRegistrationBean 组件都会被配置到Tomcat服务器中,这些组件中配置的Servlet/Filter/Listener 等Web原生组件都能映射客户端发来的请求。【源码分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true) public class MyRegistConfig @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet () MyServlet myServlet = new MyServlet(); return new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet,"/my" ,"/my02" ); } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter () MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter(); FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/my" ,"/css/*" )); return filterRegistrationBean; } @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener () MySwervletContextListener mySwervletContextListener = new MySwervletContextListener(); return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(mySwervletContextListener); } }
内嵌Servlet容器的源码分析见【Spring Boot】Spring Boot2 源码分析
内嵌服务器工作原理:手动调用要启动的服务器的 start() 方法开启服务。
要想切换服务器,则导入相应的starter场景即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId > </dependency >
修改配置文件中的 server.xxx 属性(最方便)
自定义ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory 代替TomcatServletWebServerFactory ,并将其注册到容器中
实现 WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory> ,把配置文件的值和ServletWebServerFactory 进行绑定(xxxxxCustomizer :定制化器,可以改变xxxx的默认规则):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Component public class MyTomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer <TomcatServletWebServerFactory > @Override public void customize (TomcatServletWebServerFactory server) server.addConnectorCustomizers((connector) -> connector.setAsyncTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(20 ).toMillis())); } }
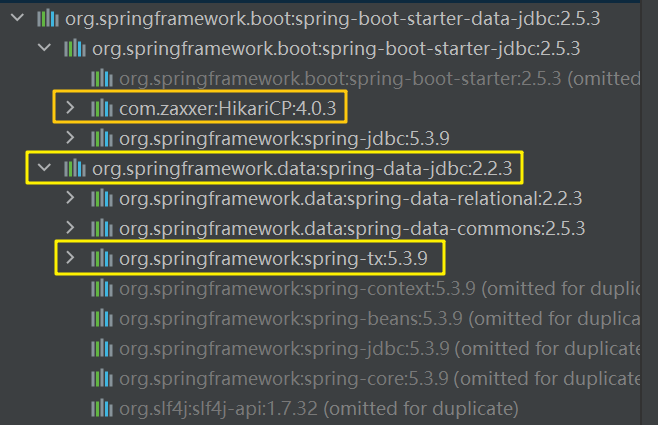
在Maven中导入JDBC场景spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId > </dependency >
导入该场景后,将出现数据源Hikari、JDBC和事务等依赖:
导入数据库MySQL驱动的依赖:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > </dependency >
Spring Boot提供的MySQL驱动的默认版本:<mysql.version>8.0.22</mysql.version>
若想要修改版本,可以:
直接依赖引入具体版本(maven的就近依赖原则)
重新声明版本(maven的属性的就近优先原则)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <properties > <java.version > 1.8</java.version > <mysql.version > 5.1.49</mysql.version > </properties > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 5.1.49 </version > </dependency >
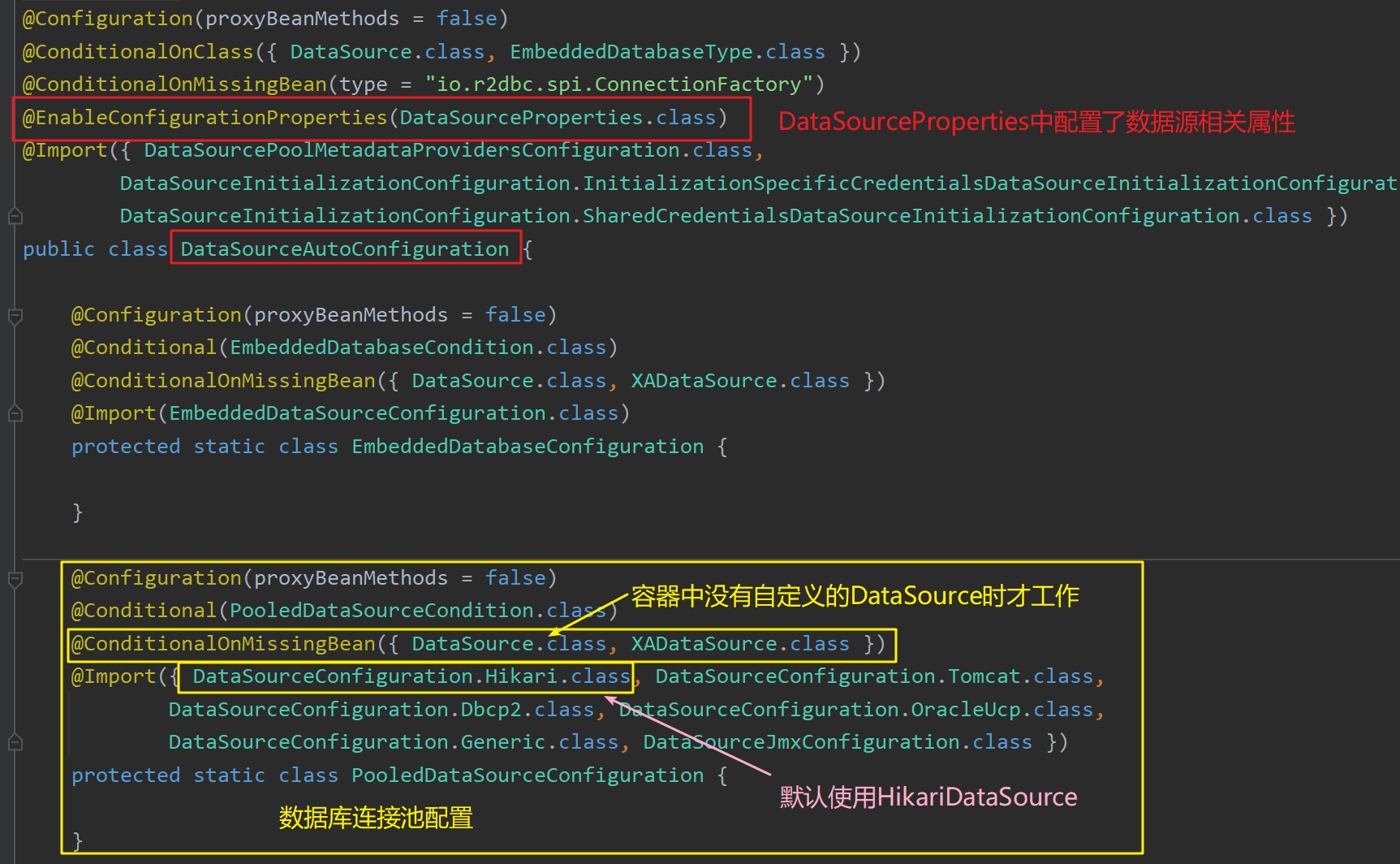
DataSourceAutoConfiguration : 数据源的自动配置类
修改数据源 相关的配置前缀:"spring.datasource"
数据库连接池 的配置,是容器中没有自定义的DataSource时 才自动配置的底层自动配置的数据源是:HikariDataSource
修改数据源 的配置项:
1 2 3 4 5 6 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true username: root password: zhaoyuyun driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
其他数据库相关的自动配置类:
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration : 事务管理器的自动配置JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration : JdbcTemplate的自动配置,可以来对数据库进行crud。容器中有JdbcTemplate 这个组件,可以修改配置前缀 "spring.jdbc" 来修改JdbcTemplate的配置。JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration : jndi的自动配置XADataSourceAutoConfiguration : 分布式事务相关的
Druid官方github地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid
若在容器中配置了自定义的数据源,则不再开启HikariDataSource 数据源。
引入Druid数据源的依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.1.17</version > </dependency >
向容器中注册Druid数据源,并开启监控、防火墙等功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @Configuration public class MyDataSourceConfig @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource dataSource () throws SQLException DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource(); druidDataSource.setFilters("stat, wall" ); return druidDataSource; } @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet () StatViewServlet statViewServlet = new StatViewServlet(); ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(statViewServlet, "/druid/*" ); registrationBean.addInitParameter("loginUsername" , "admin" ); registrationBean.addInitParameter("loginPassword" , "123456" ); return registrationBean; } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter () WebStatFilter webStatFilter = new WebStatFilter(); FilterRegistrationBean<WebStatFilter> filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(webStatFilter); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*" )); filterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("exclusions" , "*.js, *.gif, *.jpg, *.css, *.ico, /druid/*" ); return null ; } }
配置文件中设置数据源属性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myDB?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true username: root password: zhaoyuyun driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver filters: stat, wall max-active: 12
StatViewServlet 的用途包括:
提供监控信息展示的html页面
提供监控信息的JSON API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <servlet > <servlet-name > DruidStatView</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > DruidStatView</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /druid/*</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
用于统计监控信息;如SQL监控、URI监控。需要给数据源中配置属性。可以允许多个filter,多个用,分割。例如:
1 <property name="filters" value="stat,slf4j" />
Druid系统中所有filter:
别名
Filter类名
default
com.alibaba.druid.filter.stat.StatFilter
stat
com.alibaba.druid.filter.stat.StatFilter
mergeStat
com.alibaba.druid.filter.stat.MergeStatFilter
encoding
com.alibaba.druid.filter.encoding.EncodingConvertFilter
log4j
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.Log4jFilter
log4j2
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.Log4j2Filter
slf4j
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.Slf4jLogFilter
commonlogging
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.CommonsLogFilter
引入Druid官方提供的starter场景依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.1.17</version > </dependency >
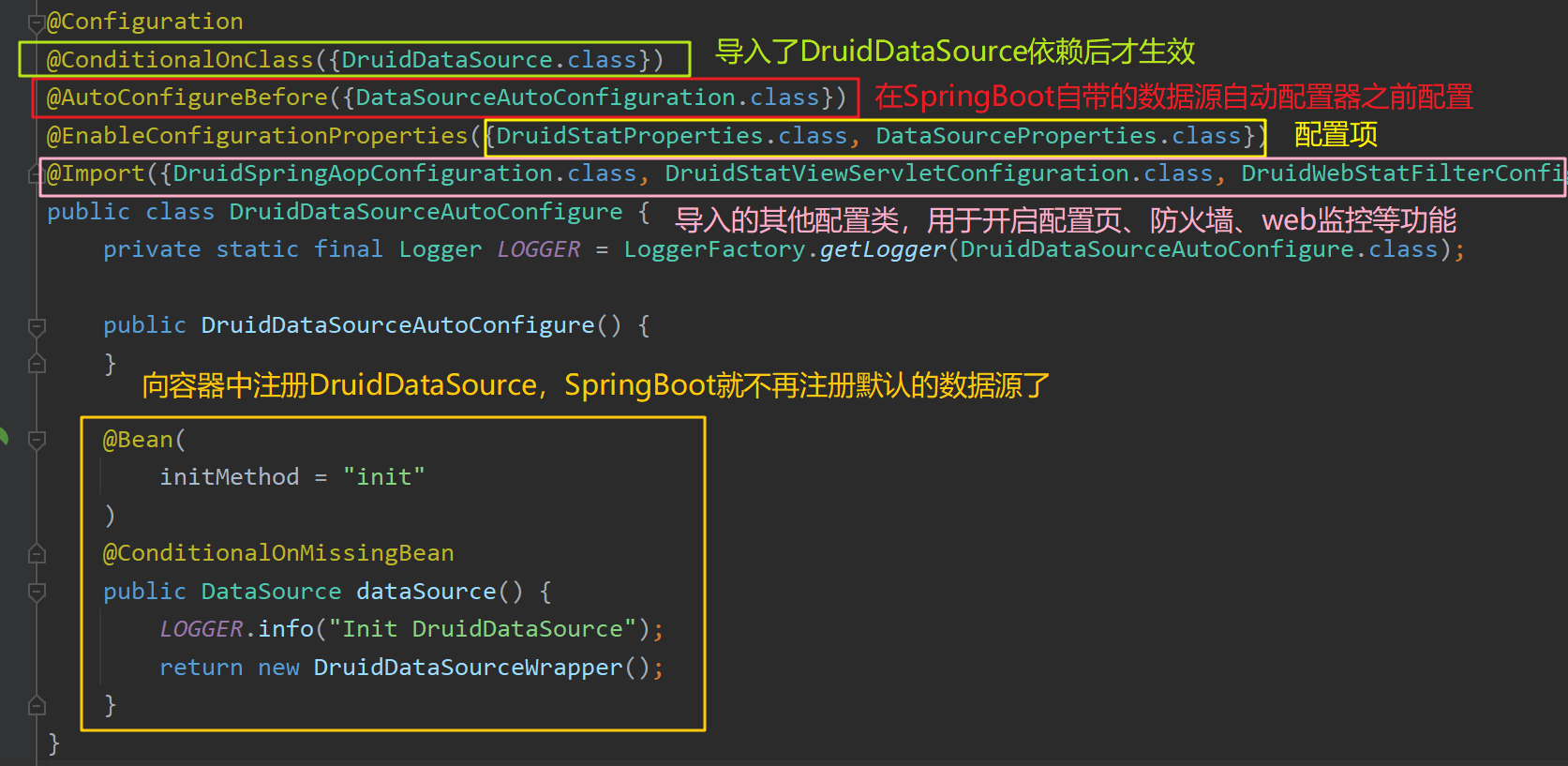
其向容器中添加了一个Druid数据源自动配置类DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure :
该配置器在Spring Boot自带的数据源自动配置器DataSourceAutoConfiguration 之前配置,因此不再注册Spring Boot默认的数据源HikariDataSource 。
该配置器绑定了DataSourceProperties 和DruidStatProperties 资源配置类,分别对应资源路径"spring.datasource"和"spring.datasource.druid"
该配置器导入了其他相关的配置类,用于开启配置页、防火墙、Web监控等功能
导入的其他相关配置类如下:
DruidSpringAopConfiguration.class (spring.datasource.druid.aop-patterns):监控Spring BeanDruidStatViewServletConfiguration.class (spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet):配置监控页:DruidWebStatFilterConfiguration.class (spring.datasource.druid.web-stat-filter):Web监控配置DruidFilterConfiguration.class :配置Druid的所有Filters:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private static final String FILTER_STAT_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat" ;private static final String FILTER_CONFIG_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.config" ;private static final String FILTER_ENCODING_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.encoding" ;private static final String FILTER_SLF4J_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j" ;private static final String FILTER_LOG4J_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.log4j" ;private static final String FILTER_LOG4J2_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.log4j2" ;private static final String FILTER_COMMONS_LOG_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.commons-log" ;private static final String FILTER_WALL_PREFIX = "spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall" ;
配置示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account username: root password: 123456 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver druid: aop-patterns: com.zhao.admin.* filters: stat,wall stat-view-servlet: enabled: true login-username: admin login-password: admin resetEnable: false web-stat-filter: enabled: true urlPattern: /* exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*' filter: stat: slow-sql-millis: 1000 logSlowSql: true enabled: true wall: enabled: true config: drop-table-allow: false
SpringBoot配置示例:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/tree/master/druid-spring-boot-starter
配置项列表:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/DruidDataSource%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%B1%9E%E6%80%A7%E5%88%97%E8%A1%A8
MyBatis官方链接:https://github.com/mybatis
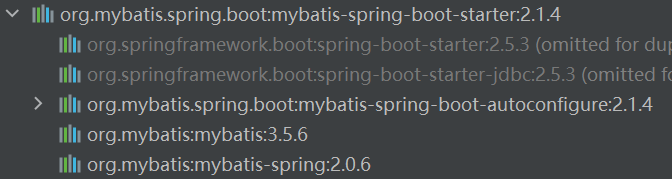
导入MyBatis的starter场景依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.1.4</version > </dependency >
其导入了如下包:
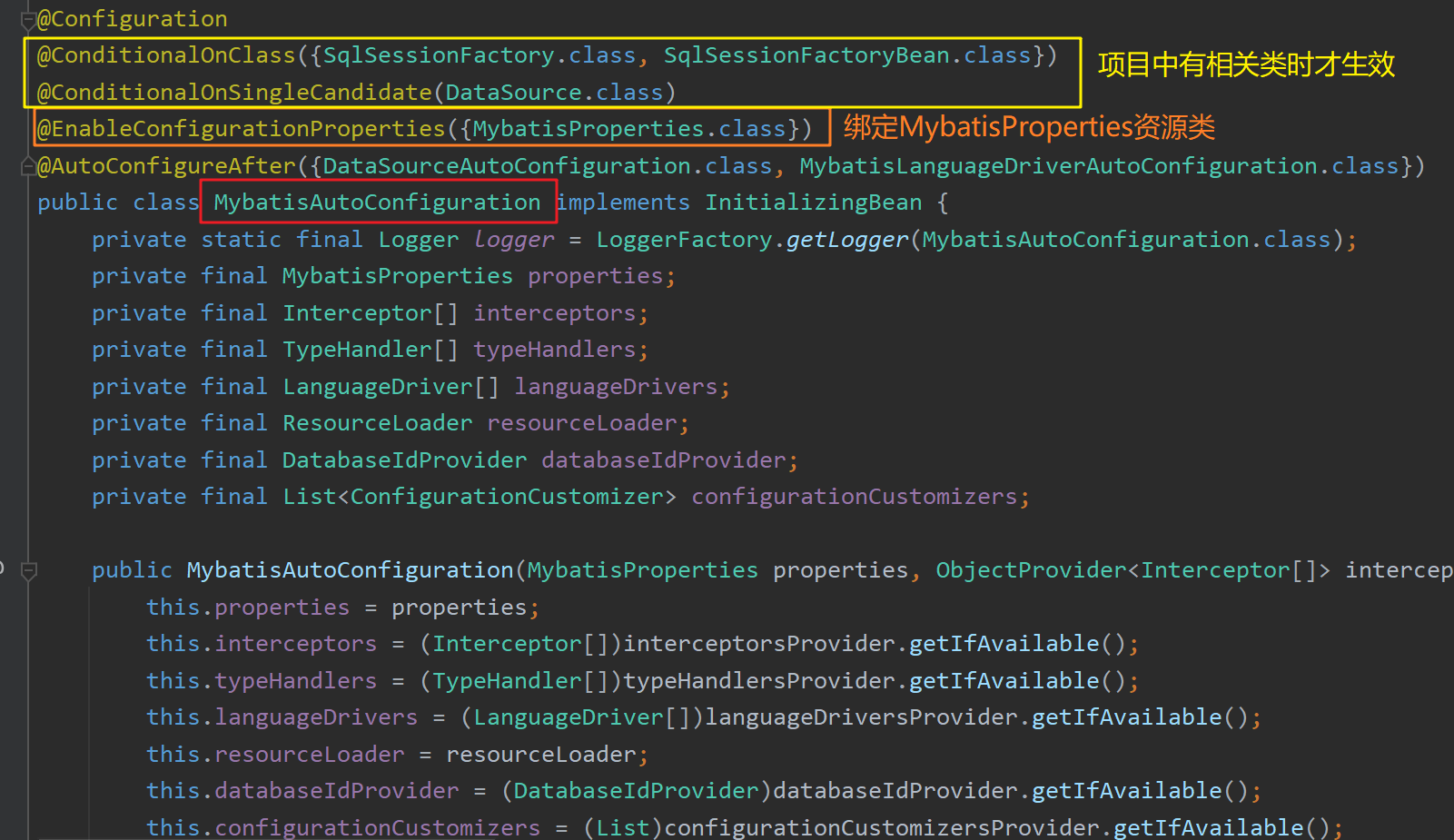
其中,MyBatis的自动配置器MybatisAutoConfiguration 会在Spring Boot启动时注册到容器中:
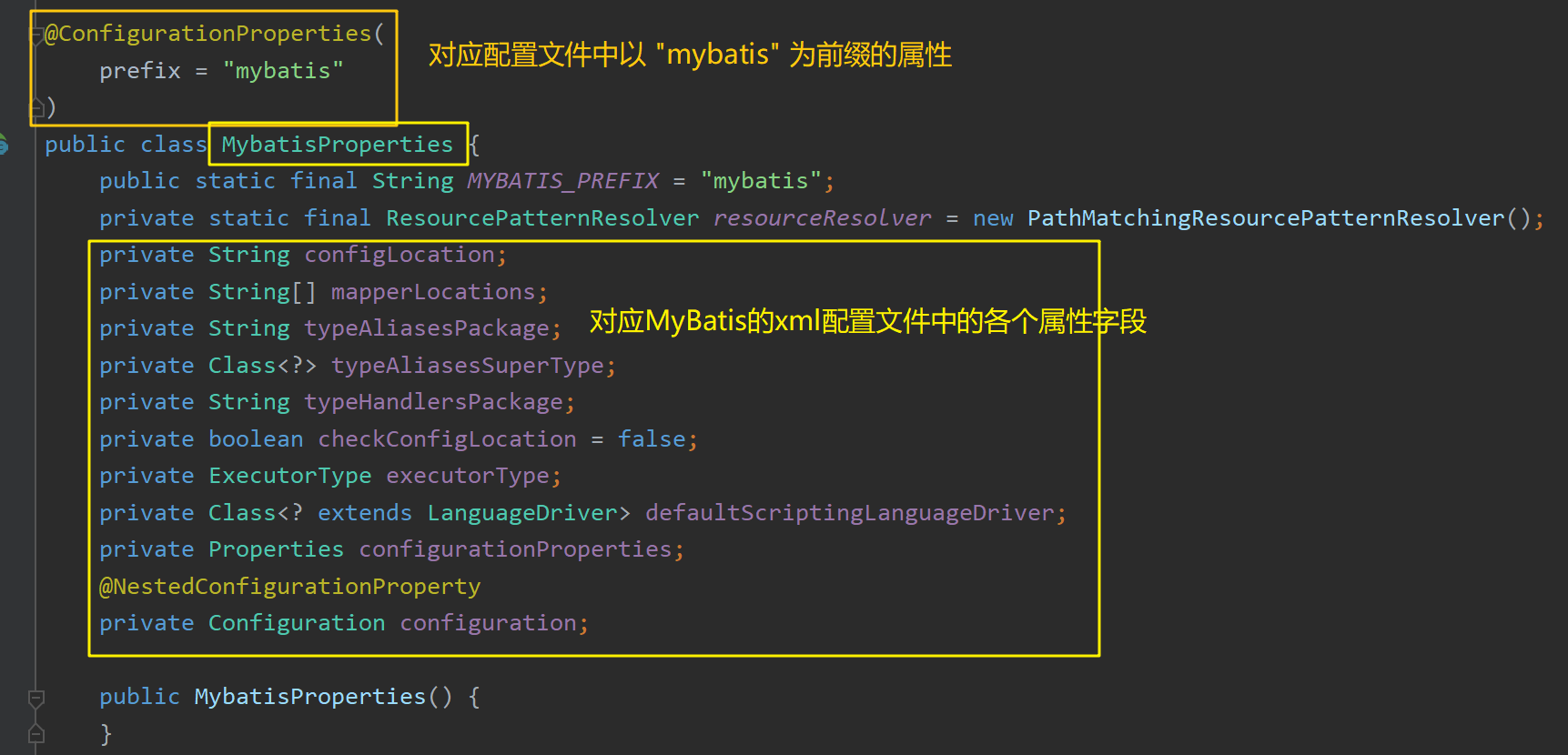
该类绑定了MybatisProperties ,对应Spring Boot的配置文件中以"mybatis"为前缀的属性:
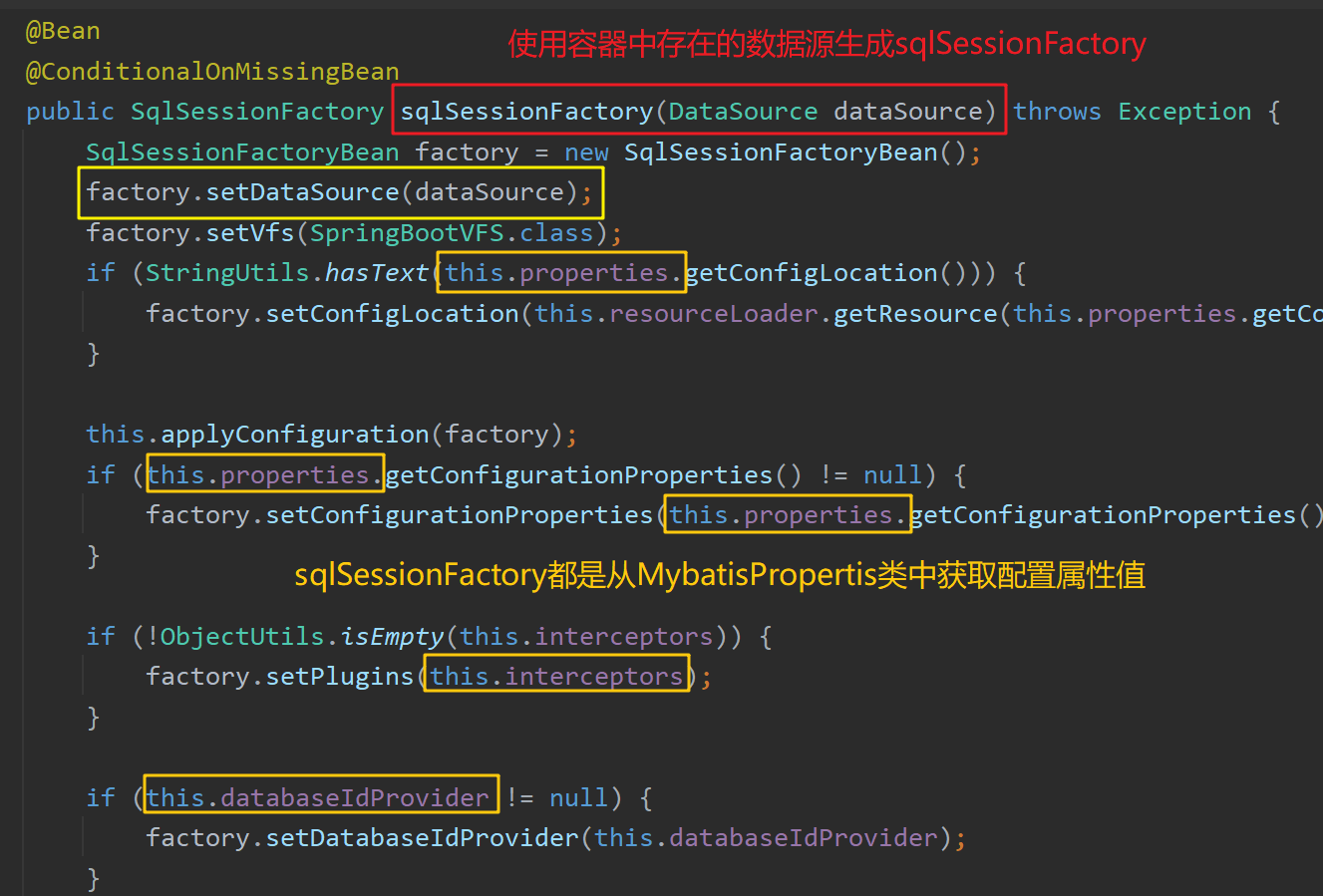
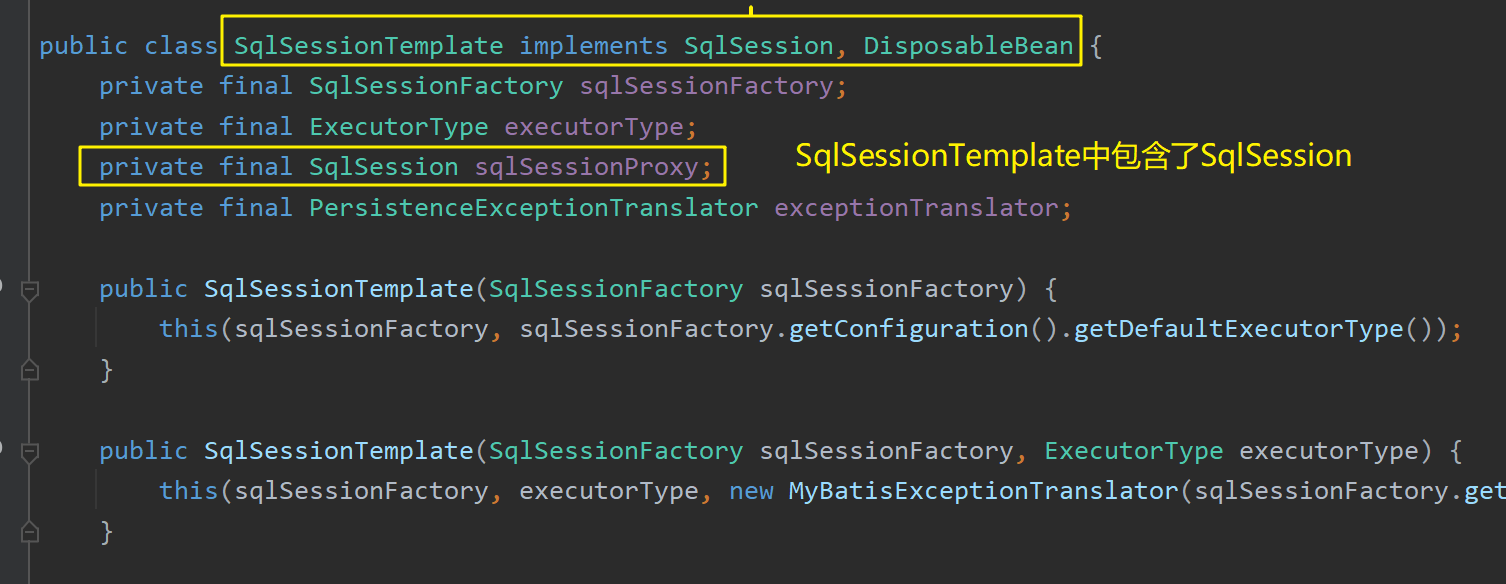
MybatisAutoConfiguration 向容器中注册了sqlSessionFactory ,其使用容器中存在的数据源,并且从配置资源类MybatisProperties 中获取MyBatis的配置属性值:
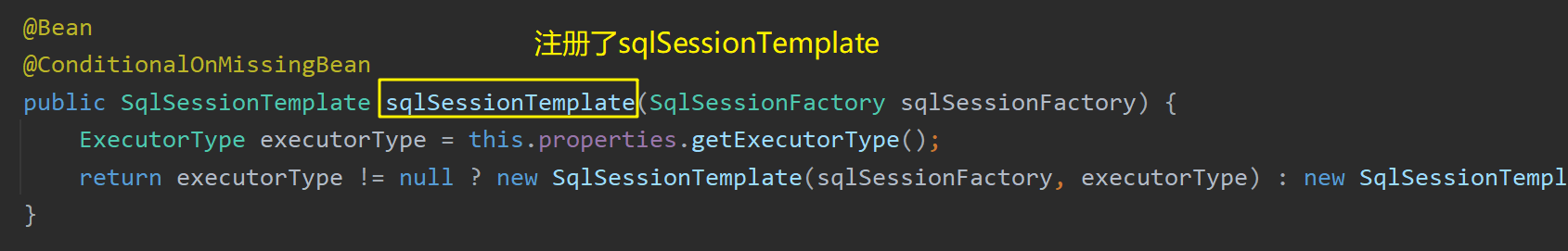
MybatisAutoConfiguration 向容器中注册了SqlSessionTemplate ,其可以执行批量的SqlSession :
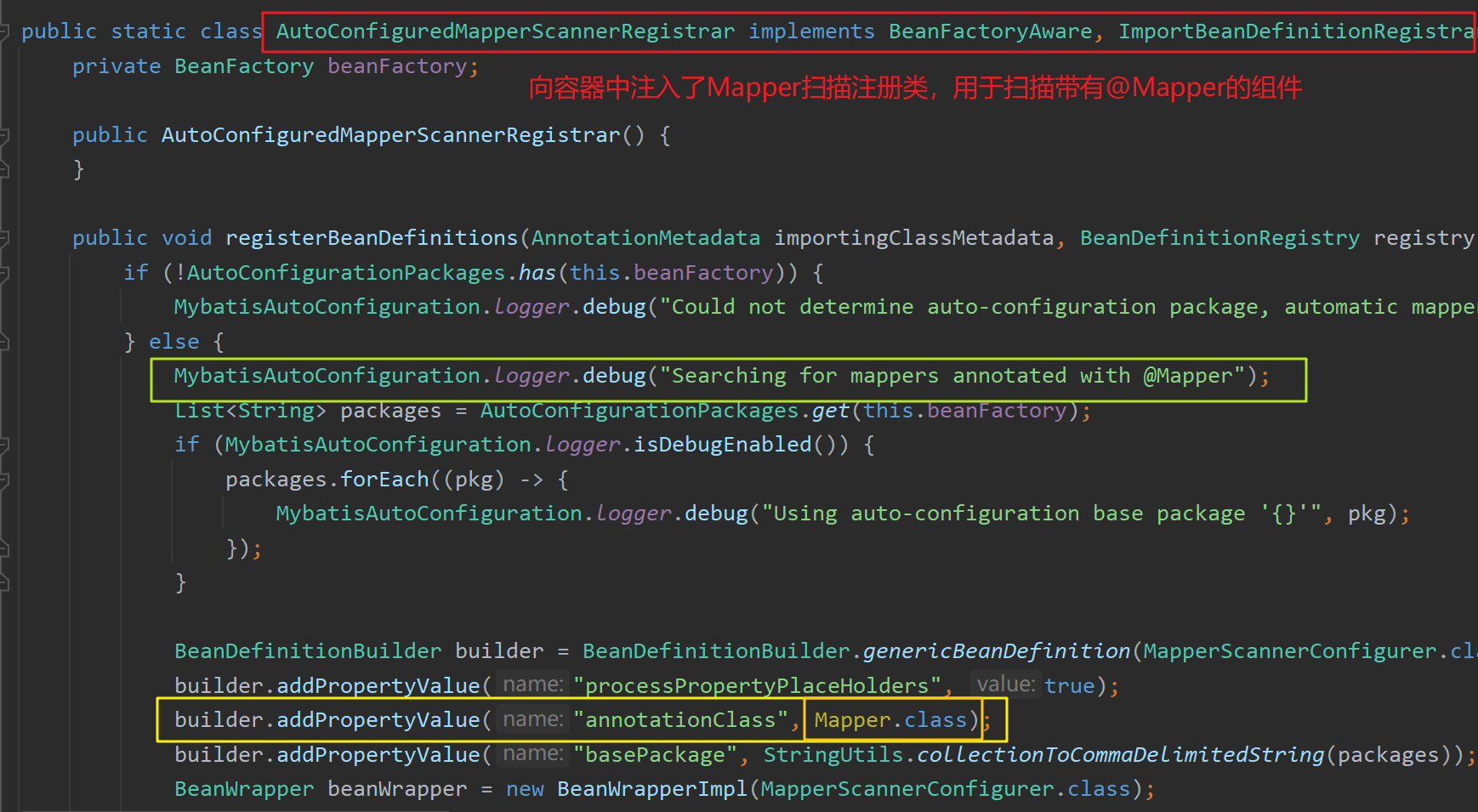
MybatisAutoConfiguration 向容器中注册了AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar ,其用于扫描容器中带有 @Mapper 注解的组件:
开启MyBatis流程:
导入MyBatis官方starter场景: mybatis-spring-boot-starter
编写xxxMapper接口,并在其上使用 @Mapper 注解(也可以使用 @MapperScan() 简化)
编写sql映射文件xxxMapper.xml(放置在classpath:mapper/*.xml下)并绑定xxxMapper接口
在application.yaml中指定mapper配置文件的位置mapper-locations,以及指定全局配置文件的信息
具体步骤如下:
导入MyBatis的starter场景: mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.1.4</version > </dependency >
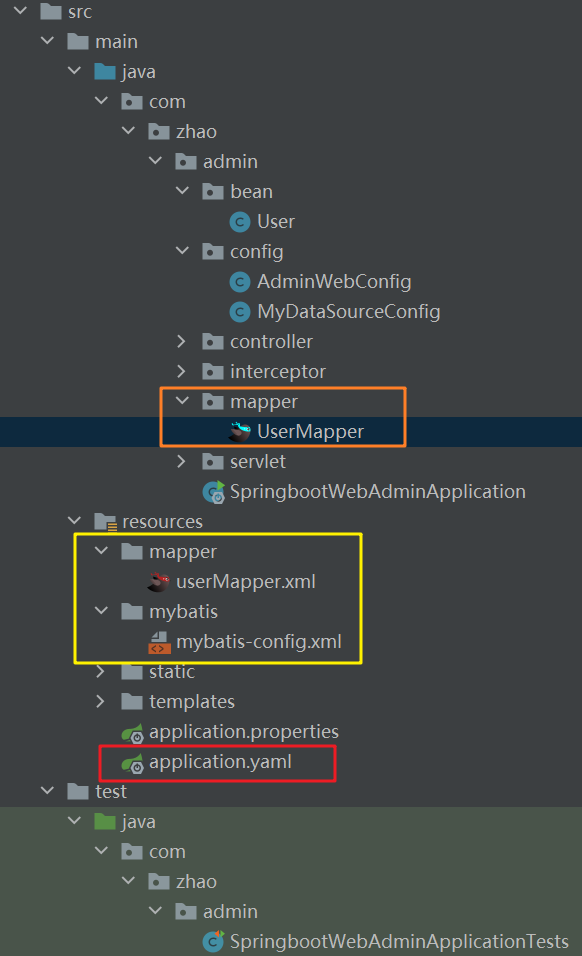
编写UserMapper接口,并在其上使用 @Mapper 注解(也可以使用 @MapperScan(“com.zhao.mapper”) 简化)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Mapper public interface UserMapper @Select("select * from user where id = #{id}") User selectUser (Long id) ; void deleteUser (Long id) }
编写sql映射文件userMapper.xml(放置在classpath:mapper/*.xml下)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.zhao.admin.mapper.UserMapper" > <select id ="selectUser" resultType ="com.zhao.admin.bean.User" > select * from user where id = #{id} </select > <delete id ="deleteUser" parameterType ="long" > delete from user where id = #{id} </delete > </mapper >
在application.yaml中配置MyBatis:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml configuration: map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
项目结构:
导入MyBatis-Plus的starter场景:mybatis-plus-boot-starter
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.baomidou</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.4.1</version > </dependency >
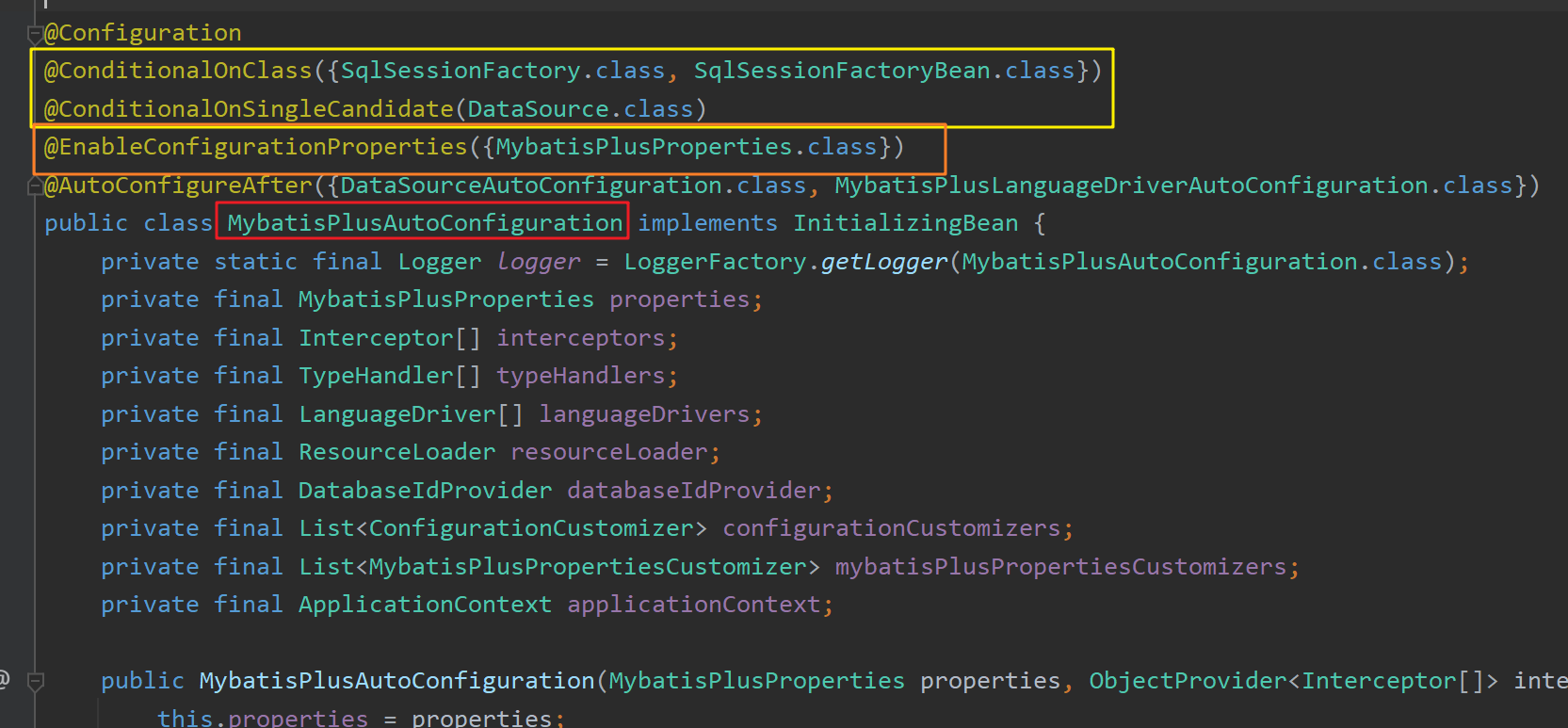
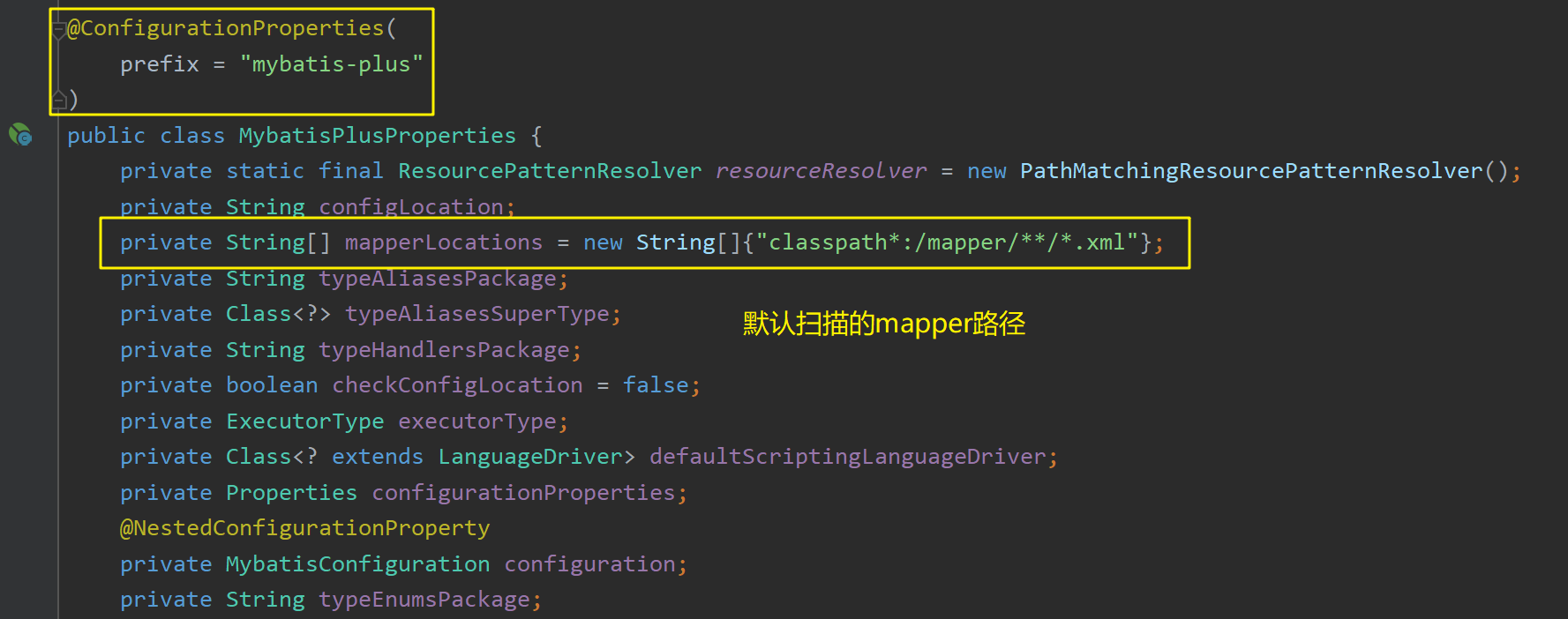
其会向容器中导入MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration :
其对应的配置前缀为"mybatis-plus",其会默认扫描"classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml",即类路径下mapper目录下的所有.xml文件都会被作为MyBatis的xml进行扫描(开发人员将sql映射文件放置在该目录下即可):
使用时,自定义的Mapper接口继承 BaseMapper<User> 接口即可自动实现简单功能的CRUD:
1 2 3 4 @Mapper public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper <User > }
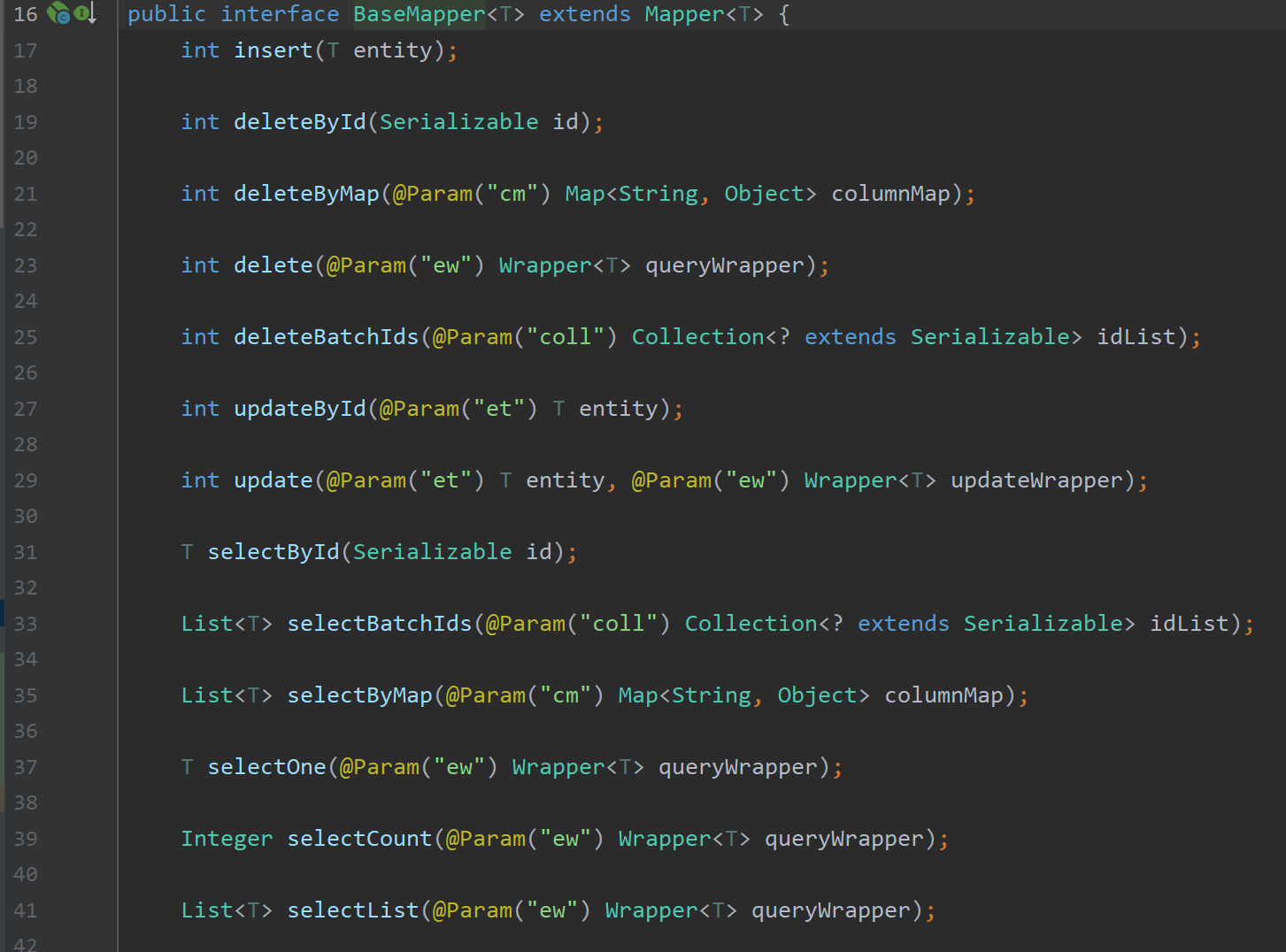
BaseMapper<User> 接口中默认实现了简单CRUD的方法:
使用MyBatis Plus提供的IService,ServiceImpl,减轻Service层开发工作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import com.zhao.hellomybatisplus.model.User;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;import java.util.List;public interface UserService extends IService <User > }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import com.zhao.hellomybatisplus.model.User;import com.zhao.hellomybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper;import com.zhao.hellomybatisplus.service.UserService;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.List;@Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl <UserMapper ,User > implements UserService }
官方文档 - Spring Boot Actuator: Production-ready Features
未来每一个微服务在云上部署以后,我们都需要对其进行监控、追踪、审计、控制等。Spring Boot就抽取了Actuator场景,使得我们每个微服务快速引用即可获得生产级别的应用监控、审计等功能。
Spring Boot Actuator1.x与2.x的不同:
使用Spring Boot Actuator:
添加Maven依赖:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId > </dependency >
该场景启动器常与spring-boot-starter-web一起使用,监控web的各种指标。
暴露所有监控信息为HTTP:
1 2 3 4 5 6 management: endpoints: enabled-by-default: true web: exposure: include: '*'
访问http://localhost:8080/actuator/**。测试例子:
可视化:https://github.com/codecentric/spring-boot-admin
常用断点Endpoint:
ID
描述
auditevents
暴露当前应用程序的审核事件信息。需要一个AuditEventRepository组件。
beans
显示应用程序中所有Spring Bean的完整列表。
caches
暴露可用的缓存。
conditions
显示自动配置的所有条件信息,包括匹配或不匹配的原因。
configprops
显示所有@ConfigurationProperties。
env
暴露Spring的属性ConfigurableEnvironment
flyway
显示已应用的所有Flyway数据库迁移。 需要一个或多个Flyway组件。
health
显示应用程序运行状况信息。
httptrace
显示HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最近100个HTTP请求-响应)。需要一个HttpTraceRepository组件。
info
显示应用程序信息。
integrationgraph
显示Spring integrationgraph 。需要依赖spring-integration-core。
loggers
显示和修改应用程序中日志的配置。
liquibase
显示已应用的所有Liquibase数据库迁移。需要一个或多个Liquibase组件。
metrics
显示当前应用程序的“指标”信息。
mappings
显示所有@RequestMapping路径列表。
scheduledtasks
显示应用程序中的计划任务。
sessions
允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。需要使用Spring Session的基于Servlet的Web应用程序。
shutdown
使应用程序正常关闭。默认禁用。
startup
显示由ApplicationStartup收集的启动步骤数据。需要使用Spring Application进行配置BufferingApplicationStartup。
threaddump
执行线程转储。
如果应用程序是Web应用程序(Spring MVC,Spring WebFlux或Jersey),则可以使用以下附加端点:
ID
描述
heapdump
返回hprof堆转储文件。
jolokia
通过HTTP暴露JMX bean(需要引入Jolokia,不适用于WebFlux)。需要引入依赖jolokia-core。
logfile
返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置logging.file.name或logging.file.path属性)。支持使用HTTPRange标头来检索部分日志文件的内容。
prometheus
以Prometheus服务器可以抓取的格式公开指标。需要依赖micrometer-registry-prometheus。
其中最常用的Endpoint:
Health:监控状况 Metrics:运行时指标 Loggers:日志记录
健康检查端点,我们一般用于在云平台,平台会定时的检查应用的健康状况,我们就需要Health Endpoint可以为平台返回当前应用的一系列组件健康状况的集合。重要的几点:
health endpoint返回的结果,应该是一系列健康检查后的一个汇总报告。
很多的健康检查默认已经自动配置好了,比如:数据库、redis等。
可以很容易的添加自定义的健康检查机制。
提供详细的、层级的、空间指标信息,这些信息可以被pull(主动推送)或者push(被动获取)方式得到:
通过Metrics对接多种监控系统。
简化核心Metrics开发。
添加自定义Metrics或者扩展已有Metrics。
默认所有的Endpoint除过shutdown都是开启的。
需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint。配置模式为management.endpoint.<endpointName>.enabled = true:
1 2 3 4 management: endpoint: beans: enabled: true
或者禁用所有的Endpoint然后手动开启指定的Endpoint:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 management: endpoints: enabled-by-default: false endpoint: beans: enabled: true health: enabled: true
支持的暴露方式:
HTTP:默认只暴露health 和info 。
JMX:默认暴露所有Endpoint。(Java Management Extensions(Java管理扩展)的缩写,是一个为应用程序植入管理功能的框架。用户可以在任何Java应用程序中使用这些代理和服务实现管理。)
除过health和info,剩下的Endpoint都应该进行保护访问。如果引入Spring Security,则会默认配置安全访问规则。
ID
JMX
Web
auditeventsYes
No
beansYes
No
cachesYes
No
conditionsYes
No
configpropsYes
No
envYes
No
flywayYes
No
healthYes
Yes
heapdumpN/A
No
httptraceYes
No
infoYes
Yes
integrationgraphYes
No
jolokiaN/A
No
logfileN/A
No
loggersYes
No
liquibaseYes
No
metricsYes
No
mappingsYes
No
prometheusN/A
No
scheduledtasksYes
No
sessionsYes
No
shutdownYes
No
startupYes
No
threaddumpYes
No
1 2 3 4 management: health: enabled: true show-details: always
通过实现HealthIndicator接口,或继承MyComHealthIndicator类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator @Override public Health health () int errorCode = check(); if (errorCode != 0 ) { return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code" , errorCode).build(); } return Health.up().build(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Component public class MyComHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator @Override protected void doHealthCheck (Health.Builder builder) throws Exception Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); if (1 == 2 ){ builder.status(Status.UP); map.put("count" ,1 ); map.put("ms" ,100 ); }else { builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE); map.put("err" ,"连接超时" ); map.put("ms" ,3000 ); } builder.withDetail("code" ,100 ) .withDetails(map); } }
方式1:编写配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 info: appName: boot-admin version: 2.0 .1 mavenProjectName: @project.artifactId@ mavenProjectVersion: @project.version@
方式2:编写InfoContributor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import java.util.Collections;import org.springframework.boot.actuate.info.Info;import org.springframework.boot.actuate.info.InfoContributor;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component public class ExampleInfoContributor implements InfoContributor @Override public void contribute (Info.Builder builder) builder.withDetail("example" , Collections.singletonMap("key" , "value" )); } }
http://localhost:8080/actuator/info
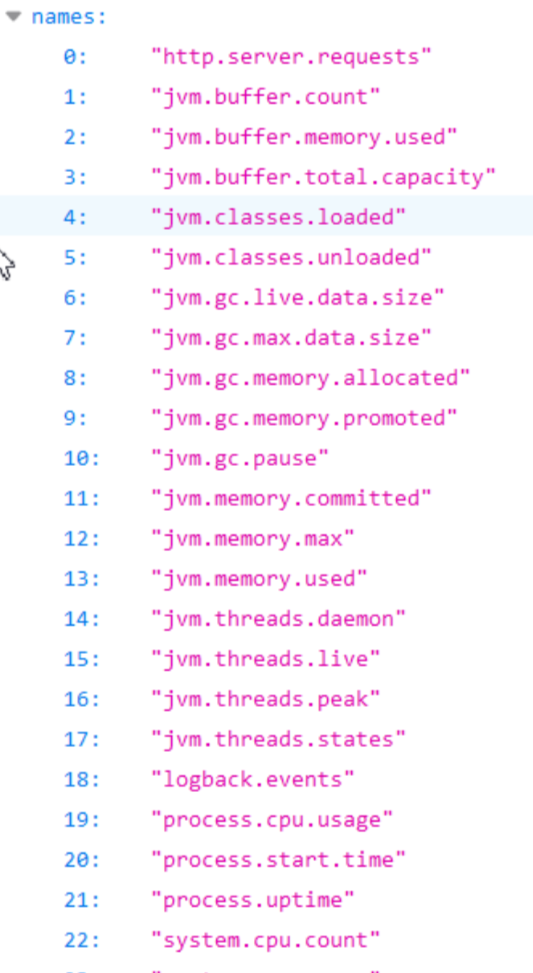
Spring Boot支持的metrics
增加定制Metrics:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class MyService Counter counter; public MyService (MeterRegistry meterRegistry) counter = meterRegistry.counter("myservice.method.running.counter" ); } public void hello () counter.increment(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean MeterBinder queueSize (Queue queue) { return (registry) -> Gauge.builder("queueSize" , queue::size).register(registry); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Component @Endpoint(id = "container") public class DockerEndpoint @ReadOperation public Map getDockerInfo () return Collections.singletonMap("info" ,"docker started..." ); } @WriteOperation private void restartDocker () System.out.println("docker restarted...." ); } }
场景:
开发ReadinessEndpoint来管理程序是否就绪。
开发LivenessEndpoint来管理程序是否存活。
官方Github 官方文档 开始使用方法
为了方便多环境适配,Spring Boot简化了profile功能。
默认配置文件application.yaml任何时候都会加载。
指定环境配置文件application-{env}.yaml,env通常替代为test,
激活指定环境:
配置文件激活:spring.profiles.active=prod
命令行激活:java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod --person.name=haha(修改配置文件的任意值,命令行优先 )
默认配置与环境配置同时生效
同名配置项,profile配置优先
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Data @Component @ConfigurationProperties("person") public class Person private String name; private Integer age; }
application.yaml:
1 2 3 person: name: zhangsan age: 8
多环境配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public interface Person String getName () ; Integer getAge () ; } @Profile("test") @Component @ConfigurationProperties("person") @Data public class Worker implements Person private String name; private Integer age; } @Profile(value = {"prod","default"}) @Component @ConfigurationProperties("person") @Data public class Boss implements Person private String name; private Integer age; }
application-test.yaml:
1 2 3 4 5 person: name: test-张三 server: port: 7000
application-prod.yaml:
1 2 3 4 5 person: name: prod-张三 server: port: 8000
application.properties:
1 2 spring.profiles.active =prod
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Autowired private Person person;@GetMapping("/") public String hello () return person.getClass().toString(); }
@Profile 还可以修饰在方法上:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Color } @Configuration public class MyConfig @Profile("prod") @Bean public Color red () return new Color(); } @Profile("test") @Bean public Color green () return new Color(); } }
可以激活一组:
1 2 3 4 spring.profiles.active =production spring.profiles.group.production[0] =proddb spring.profiles.group.production[1] =prodmq
官方文档 - Externalized Configuration
Spring Boot uses a very particular PropertySource order that is designed to allow sensible overriding of values. Properties are considered in the following order (with values from lower items overriding earlier ones)(1优先级最低,14优先级最高)
Default properties (specified by setting SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties).
@PropertySource annotations on your @Configuration classes. Please note that such property sources are not added to the Environment until the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such as logging.* and spring.main.* which are read before refresh begins.Config data (such as application.properties files)
A RandomValuePropertySource that has properties only in random.*.
OS environment variables.
Java System properties (System.getProperties()).
JNDI attributes from java:comp/env.
ServletContext init parameters.ServletConfig init parameters.Properties from SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON (inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property).
Command line arguments.
properties attribute on your tests. Available on @SpringBootTest and the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.@TestPropertySource annotations on your tests.Devtools global settings properties in the $HOME/.config/spring-boot directory when devtools is active.
指定环境变量优先,外部优先,后加载的可以覆盖前面的同名配置项。
外部配置源
Java属性文件
YAML文件
环境变量
命令行参数
配置文件查找位置
classpath 根路径classpath 根路径下config目录jar包当前目录
jar包当前目录的config目录
/config子目录的直接子目录
配置文件加载顺序:
当前jar包内部的application.properties和application.yml
当前jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
引用的外部jar包的application.properties和application.yml
引用的外部jar包的application-{profile}.properties和application-{profile}.yml
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库 。作为最新版本的JUnit框架,JUnit5与之前版本的JUnit框架有很大的不同。由三个不同子项目的几个不同模块组成:
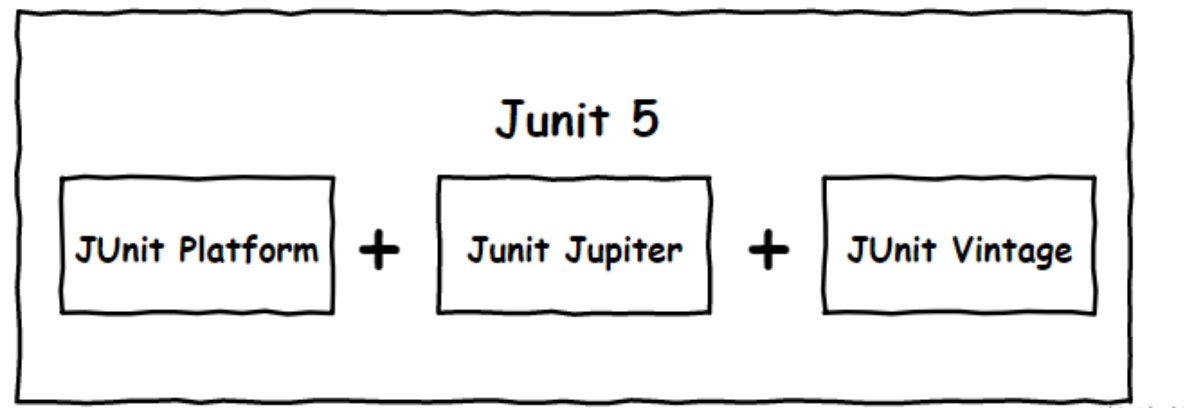
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform : JUnit Platform是在JVM上启动测试框架的基础,不仅支持JUnit自制的测试引擎,其他测试引擎也都可以接入。JUnit Jupiter : JUnit Jupiter提供了JUnit5的新的编程模型,是JUnit5新特性的核心。内部包含了一个测试引擎 ,用于在JUnit Platform上运行。JUnit Vintage : 由于JUint已经发展多年,为了照顾老的项目,JUnit Vintage提供了兼容JUnit4.x和JUnit3.x的测试引擎。
注意:Spring Boot 2.4 以上版本移除了默认对Vintage的依赖。如果需要兼容junit4需要自行引入(不能使用junit4的功能 @Test)
JUnit 5’s Vintage Engine Removed from spring-boot-starter-test,如果需要继续兼容junit4需要自行引入vintage:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <dependency > <groupId > org.junit.vintage</groupId > <artifactId > junit-vintage-engine</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.hamcrest</groupId > <artifactId > hamcrest-core</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency >
现在版本使用 @SpringBootTest :
1 2 3 4 5 6 @SpringBootTest class Boot05WebAdminApplicationTests @Test void contextLoads () } }
以前版本使用 @SpringBootTest + @RunWith(SpringTest.class)
Spring Boot整合JUnit以后:
编写测试方法:@Test标注(注意需要使用JUnit5版本的注解)
JUnit类具有Spring的功能,@Autowired、比如 @Transactional 标注测试方法,测试完成后自动回滚
JUnit 5 的 Maven 依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.junit.jupiter</groupId > <artifactId > junit-jupiter-api</artifactId > <version > 5.3.2</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency >
JUnit5的注解与JUnit4的注解有所变化:https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests-annotations
@Test 表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试@ParameterizedTest 表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍@RepeatedTest 表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍@DisplayName 为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称@BeforeEach 表示在每个单元测试之前执行@AfterEach 表示在每个单元测试之后执行@BeforeAll 表示在所有单元测试之前执行@AfterAll 表示在所有单元测试之后执行@Tag 表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的 @Categories @Disabled 表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的 @Ignore @Timeout 表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误@ExtendWith 为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; public class TestDemo @Test @DisplayName("第一次测试") public void firstTest () System.out.println("hello world" ); } }
断言(Assertions)是测试方法中的核心部分,用来对测试需要满足的条件进行验证。这些断言方法都是 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 的静态方法 。
断言用于检查业务逻辑返回的数据是否合理。所有的测试运行结束以后,会有一个详细的测试报告
用来对单个值进行简单的验证。如:
方法
说明
assertEquals
判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否相等
assertNotEquals
判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否不相等
assertSame
判断两个对象引用是否指向同一个对象
assertNotSame
判断两个对象引用是否指向不同的对象
assertTrue
判断给定的布尔值是否为 true
assertFalse
判断给定的布尔值是否为 false
assertNull
判断给定的对象引用是否为 null
assertNotNull
判断给定的对象引用是否不为 null
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Test @DisplayName("simple assertion") public void simple () assertEquals(3 , 1 + 2 , "simple math" ); assertNotEquals(3 , 1 + 1 ); assertNotSame(new Object(), new Object()); Object obj = new Object(); assertSame(obj, obj); assertFalse(1 > 2 ); assertTrue(1 < 2 ); assertNull(null ); assertNotNull(new Object()); }
通过 assertArrayEquals() 方法来判断两个对象或原始类型的数组是否相等
1 2 3 4 5 @Test @DisplayName("array assertion") public void array () assertArrayEquals(new int []{1 , 2 }, new int [] {1 , 2 }); }
assertAll() 方法接受多个 org.junit.jupiter.api.Executable 函数式接口的实例作为要验证的断言,可以通过 lambda 表达式很容易的提供这些断言
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test @DisplayName("assert all") public void all () assertAll("Math" , () -> assertEquals(2 , 1 + 1 ), () -> assertTrue(1 > 0 ) ); }
在JUnit4时期,想要测试方法的异常情况时,需要用 @Rule 注解的ExpectedException变量,还是比较麻烦的。而JUnit5提供了一种新的断言方式 Assertions.assertThrows() ,配合函数式编程就可以进行使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Test @DisplayName("异常测试") public void exceptionTest () ArithmeticException exception = Assertions.assertThrows( ArithmeticException.class, () -> System.out.println(1 % 0 )); }
JUnit5还提供了 Assertions.assertTimeout() 为测试方法设置了超时时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test @DisplayName("超时测试") public void timeoutTest () Assertions.assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(1000 ), () -> Thread.sleep(500 )); }
通过 fail() 方法直接使得测试失败
1 2 3 4 5 @Test @DisplayName("fail") public void shouldFail () fail("This should fail" ); }
JUnit 5 中的前置条件(Assumptions【假设】 )类似于断言,不同之处在于不满足的断言会使得测试方法失败 ,而不满足的前置条件只会使得测试方法的执行终止 。前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当该前提不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @DisplayName("前置条件") public class AssumptionsTest private final String environment = "DEV" ; @Test @DisplayName("simple") public void simpleAssume () assumeTrue(Objects.equals(this .environment, "DEV" )); assumeFalse(() -> Objects.equals(this .environment, "PROD" )); } @Test @DisplayName("assume then do") public void assumeThenDo () assumingThat( Objects.equals(this .environment, "DEV" ), () -> System.out.println("In DEV" ) ); } }
assumeTrue() 和 assumFalse() 确保给定的条件为 true 或 false,不满足条件会使得测试 执行终止(不会失败) 。
assumingThat() 的参数是表示条件的布尔值和对应的 Executable 接口的实现对象。只有条件满足时,Executable 对象才会被执行;当条件不满足时,测试执行并不会终止。
JUnit 5 可以通过 Java 中的内部类和 @Nested 注解实现嵌套测试,从而可以更好的把相关的测试方法组织在一起。在内部类中可以使用 @BeforeEach 和 @AfterEach 注解,而且嵌套的层次没有限制。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 @DisplayName("A stack") class TestingAStackDemo Stack<Object> stack; @Test @DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()") void isInstantiatedWithNew () new Stack<>(); } @Nested @DisplayName("when new") class WhenNew @BeforeEach void createNewStack () stack = new Stack<>(); } @Test @DisplayName("is empty") void isEmpty () assertTrue(stack.isEmpty()); } @Test @DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped") void throwsExceptionWhenPopped () assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop); } @Test @DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked") void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked () assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek); } @Nested @DisplayName("after pushing an element") class AfterPushing String anElement = "an element" ; @BeforeEach void pushAnElement () stack.push(anElement); } @Test @DisplayName("it is no longer empty") void isNotEmpty () assertFalse(stack.isEmpty()); } @Test @DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty") void returnElementWhenPopped () assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop()); assertTrue(stack.isEmpty()); } @Test @DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty") void returnElementWhenPeeked () assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek()); assertFalse(stack.isEmpty()); } } } }
参数化测试是JUnit5很重要的一个新特性,它使得用不同的参数多次运行测试成为了可能,也为我们的单元测试带来许多便利。
利用 @ValueSource 等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
@ValueSource : 为参数化测试指定入参来源,支持八大基础类以及String类型,Class类型@NullSource : 表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参@EnumSource : 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参@CsvFileSource :表示读取指定CSV文件内容作为参数化测试入参@MethodSource :表示读取指定方法的返回值作为参数化测试入参(注意方法返回需要是一个流)
当然如果参数化测试仅仅只能做到指定普通的入参还达不到让我觉得惊艳的地步。他的强大之处的地方在于他可以支持外部的各类入参。如:CSV,YML,JSON 文件甚至方法的返回值也可以作为入参。只需要去实现ArgumentsProvider 接口,任何外部文件都可以作为它的入参。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @ParameterizedTest @ValueSource(strings = {"one", "two", "three"}) @DisplayName("参数化测试1") public void parameterizedTest1 (String string) System.out.println(string); Assertions.assertTrue(StringUtils.isNotBlank(string)); } @ParameterizedTest @MethodSource("method") @DisplayName("方法来源参数") public void testWithExplicitLocalMethodSource (String name) System.out.println(name); Assertions.assertNotNull(name); } static Stream<String> method () return Stream.of("apple" , "banana" ); }
在进行迁移的时候需要注意如下变化:
注解在 org.junit.jupiter.api 包中,断言在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 类中,前置条件在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions 类中。
把 @Before 和 @After 替换成 @BeforeEach 和 @AfterEach 。
把 @BeforeClass 和 @AfterClass 替换成 @BeforeAll 和 @AfterAll 。
把 @Ignore 替换成 @Disabled 。
把 @Category 替换成 @Tag 。
把 @RunWith 、@Rule 和 @ClassRule 替换成 @ExtendWith 。