Spring Cloud Ribbon是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端负载均衡工具 。Github - Ribbon
Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法 和服务调用 。Ribbon客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。
简单地说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Balancer (简称LB)后面所有的机器,Ribbon会自动基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等)去连接这些机器。我们很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的 负载均衡算法。
Ribbon = 负载均衡 + RestTemplate调用
ribbon
Netflix的Ribbon目前也进入维护模式,未来可能被Spring Cloud LoadBalacer替代,但其目前在大量的生产环境仍然工作。
负载均衡简单地说就是将用户的请求平摊分配到多个服务上,从而达到系统的HA (高可用)。常见的负载均衡有软件Nginx,LVS,硬件F5等。
Ribbon本地负载均衡客户端 VS Nginx服务端负载均衡区别
Nginx:用来对用户发来的请求进行负载均衡,即用户发来请求访问某一台服务消费者微服务 ,Nginx基于负载均衡算法选择出合适的消费者微服务 ;
Ribbon:当用户发来的请求经过Nginx进行负载均衡后,选择了某一台服务消费者微服务 ,在调用其接口时候,消费者会从注册中心获取服务提供者微服务 的列表,再基于自己的负载均衡算法选择某一台提供者实现RPC远程服务调用。
即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,如F5,也可以是软件,如Nginx),由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方;
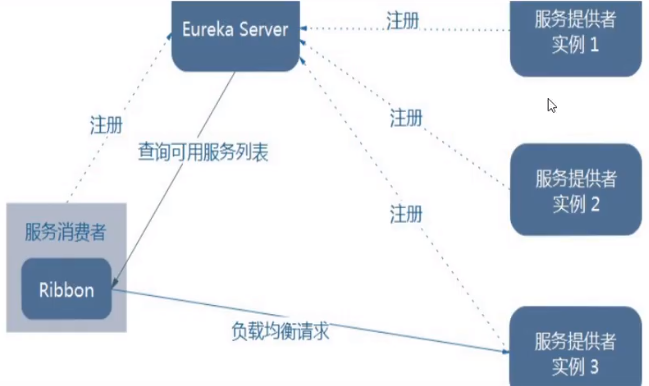
将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。
Ribbon就属于进程内LB ,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
基于Ribbon实现负载均衡的方法:在RestTemplate 对象上添加 @LoadBalanced 注解,之后调用其方法时将服务名作为URL传入,即可开启负载均衡功能。(RestTemplate 本身不具有负载均衡能力,需要开启Ribbon的注解)
总结:Ribbon其实就是一个软负载均衡的客户端组件,它可以和其他所需请求的客户端结合使用,和Eureka结合只是其中的一个实例。
Ribbon在工作时分成两步:
第一步先选择Eureka Server,它优先选择在同一个区域内负载较少 的Server;
第二步再根据用户指定的策略,从取到的服务注册列表中选择一个地址。
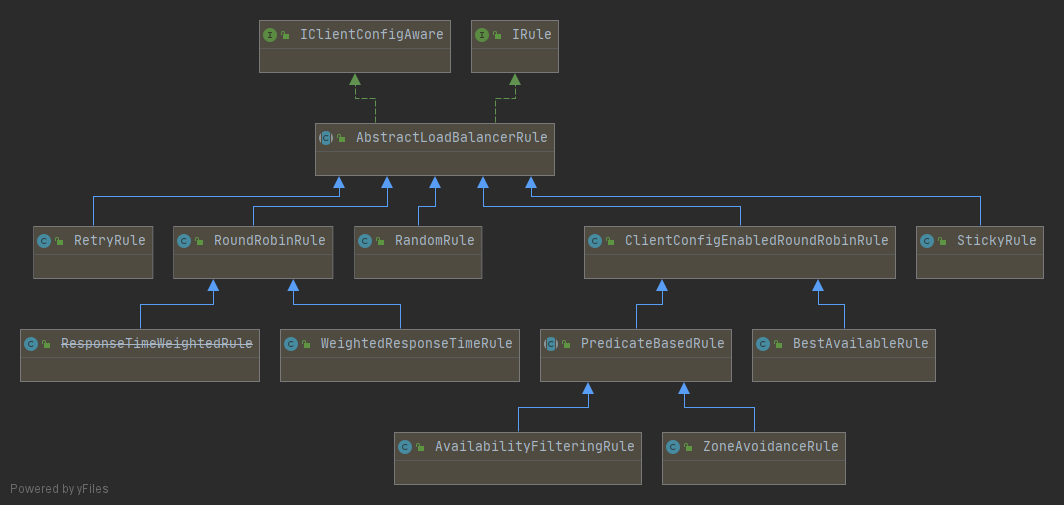
其中Ribbon提供了多种策略:比如轮询、随机和根据响应时间加权。
导入spring-cloud-starter-ribbon即可:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupld > org.springframework.cloud</groupld > <artifactld > spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactid > </dependency >
若导入了spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client,其自带spring-cloud-starter-ribbon依赖。
RestTemplate Java Doc
getForObject() / getForEntity() - GET请求方法
getForObject() :返回对象为响应体中数据转化成的对象,基本上可以理解为Json。getForEntity() :返回对象为ResponseEntity 对象,包含了响应中的一些重要信息,比如响应头、响应状态码、响应体等。
postForObject() / postForEntity() - POST请求方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/getForEntity/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getPayment2 (@PathVariable("id") Long id) ResponseEntity<CommonResult> entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/get/" +id,CommonResult.class); if (entity.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()){ return entity.getBody(); }else { return new CommonResult<>(444 ,"操作失败" ); } }
在支付服务搭建Eureka集群后,订单服务使用 @LoadBalanced 注解开启负载均衡 功能,此注解在Spring Cloud提供的LoadBalacer包下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;@Configuration public class ApplicationContextConfig @LoadBalanced @Bean public RestTemplate getRestTemplate () return new RestTemplate(); } }
此时PAYMENT_URL 需要写成支付服务对应的服务名: http://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Slf4j @RestController public class OrderController public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE" ; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping(value = "/consumer/payment/create") public CommonResult create (Payment payment) return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/create" , payment, CommonResult.class); } @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getPayment (@PathVariable("id") Long id) log.info("1211" ); return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/get/" + id, CommonResult.class); } }
此时消费者访问提供者时即开启了负载均衡功能
lRule :根据特定算法中从服务列表中选取一个要访问的服务
RoundRobinRule :轮询RandomRule :随机RetryRule :先按照RoundRobinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内会进行重WeightedResponseTimeRule :对RoundRobinRule的扩展,响应速度越快的实例选择权重越大,越容易被选择BestAvailableRule :会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务AvailabilityFilteringRule :先过滤掉故障实例,再选择并发较小的实例ZoneAvoidanceRule :默认规则 ,复合判断Server所在区域的性能和Server的可用性选择服务器
官方文档明确给出了警告:修改Ribbon负载规则的自定义配置类不能放在**@ComponentScan**所扫描的当前包下以及子包下,否则我们自定义的这个配置类就会被所有的Ribbon客户端所共享,达不到特殊化定制的目的了。(也就是说不要将Ribbon配置类与主启动类同包)
新建package - com.zhao.myrule,在com.zhao.myrule下新建MySelfRule 规则类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration public class MySelfRule @Bean public IRule myRule () return new RandomRule(); } }
主启动类添加 @RibbonClient
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import com.zhao.myrule.MySelfRule;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE", configuration = MySelfRule.class) public class OrderMain80 public static void main ( String[] args ) SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class, args); } }
在启动类上配置了 @RibbonClient 注解后,该微服务即开启了Ribbon功能,此时再使用RestTemplate 调用服务端时即开启了负载均衡功能。
默认负载轮训算法:rest接口第几次请求数 % 服务器集群总数量 = 实际调用服务器位置下标,每次服务重启动后rest接口计数从1开始 。
1 List<Servicelnstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE" );
如:
List [0] instances = 127.0.0.1:8002List [1] instances = 127.0.0.1:8001
8001 + 8002组合成为集群,它们共计2台机器,集群总数为2,按照轮询算法原理:
当总请求数为1时:1%2=1对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位2时:2%2=О对应下标位置为0,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8002
当总请求数位3时:3%2=1对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位4时:4%2=О对应下标位置为0,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8002
如此类推…
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public interface IRule public Server choose (Object key) public void setLoadBalancer (ILoadBalancer lb) public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 package com.netflix.loadbalancer;import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.util.List;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter; private static final boolean AVAILABLE_ONLY_SERVERS = true ; private static final boolean ALL_SERVERS = false ; private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RoundRobinRule.class); public RoundRobinRule () nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0 ); } public RoundRobinRule (ILoadBalancer lb) this (); setLoadBalancer(lb); } public Server choose (ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) if (lb == null ) { log.warn("no load balancer" ); return null ; } Server server = null ; int count = 0 ; while (server == null && count++ < 10 ) { List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers(); List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers(); int upCount = reachableServers.size(); int serverCount = allServers.size(); if ((upCount == 0 ) || (serverCount == 0 )) { log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb); return null ; } int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount); server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex); if (server == null ) { Thread.yield(); continue ; } if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) { return (server); } server = null ; } if (count >= 10 ) { log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb); } return server; } private int incrementAndGetModulo (int modulo) for (;;) { int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get(); int next = (current + 1 ) % modulo; if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) return next; } } @Override public Server choose (Object key) return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key); } @Override public void initWithNiwsConfig (IClientConfig clientConfig) } }